-
 KP-27F 7-inch Marine GPS Chart Plotter Marine Built-in Fish Finder depth sounder sonar fish finder With TRANSDUCERS$500.00
KP-27F 7-inch Marine GPS Chart Plotter Marine Built-in Fish Finder depth sounder sonar fish finder With TRANSDUCERS$500.00 -
 Matsutec Solenoid Pump for Autopilot Model: 1012S(12V) and 1024S(24V)$700.00
Matsutec Solenoid Pump for Autopilot Model: 1012S(12V) and 1024S(24V)$700.00 -
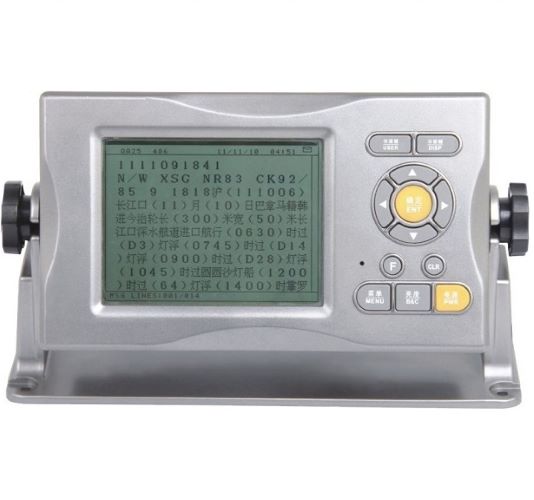 Matsutec GMDSS NAVTEX RECEIVER NTX-100B$850.00
Matsutec GMDSS NAVTEX RECEIVER NTX-100B$850.00 -
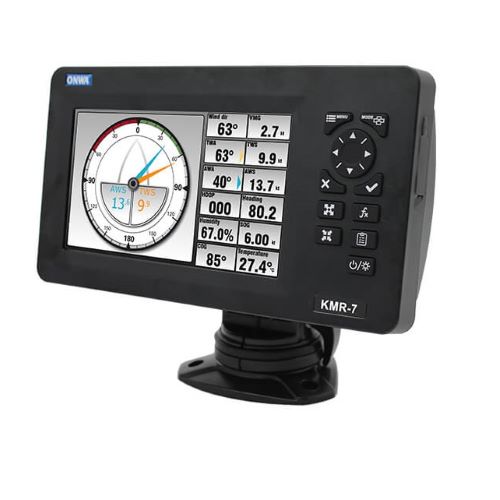 7-inch Multi-Function Display With NMEA0183 Multiplexer and NMEA2000$850.00
7-inch Multi-Function Display With NMEA0183 Multiplexer and NMEA2000$850.00 -
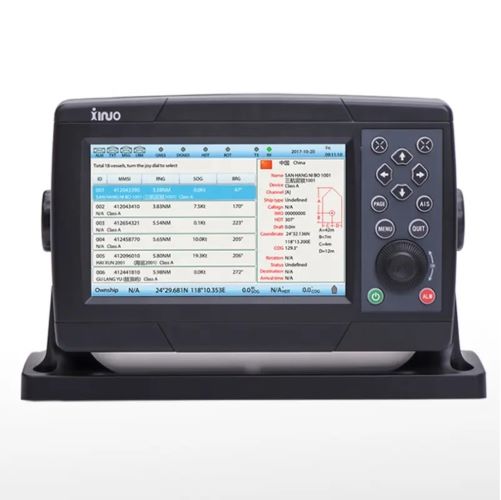 7inch display Class A AIS Transponder with ccs XA-198$0.00
7inch display Class A AIS Transponder with ccs XA-198$0.00 -
 ONWA KM-8X 5IN1 8-inch Marine Marine GPS Chart Plotter + Class B AIS Transponder + Fish Finder +marine Radar Function$3000.00
ONWA KM-8X 5IN1 8-inch Marine Marine GPS Chart Plotter + Class B AIS Transponder + Fish Finder +marine Radar Function$3000.00 -
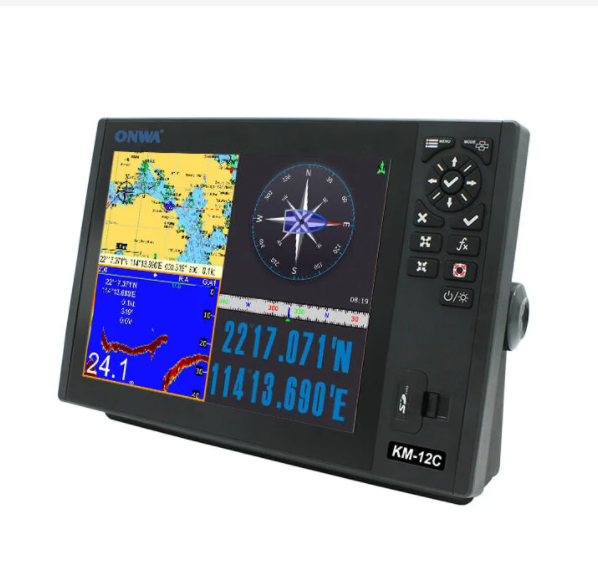 KM-12X 5 IN 1 12-inch Marine Marine GPS Chart Plotter + Class B AIS Transponder + Fish Finder +marine Radar Function$0.00
KM-12X 5 IN 1 12-inch Marine Marine GPS Chart Plotter + Class B AIS Transponder + Fish Finder +marine Radar Function$0.00 -
 KM-8C 8-inch GPS Chart Plotter with GPS Fish Finder/depth sounder/Echo sounder (supports Expanded Features)+fish transducer$2000.00
KM-8C 8-inch GPS Chart Plotter with GPS Fish Finder/depth sounder/Echo sounder (supports Expanded Features)+fish transducer$2000.00 -
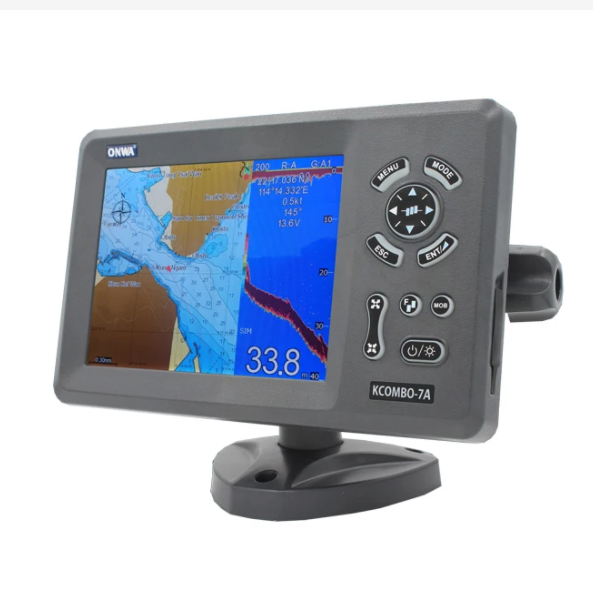 ONWA KCombo-7A 7inch marine GPS combo transducer Color LCD GPS plotter Combo with Fishfinder GPS +FISH FINDER+ Class B AIS$1200.00
ONWA KCombo-7A 7inch marine GPS combo transducer Color LCD GPS plotter Combo with Fishfinder GPS +FISH FINDER+ Class B AIS$1200.00 -
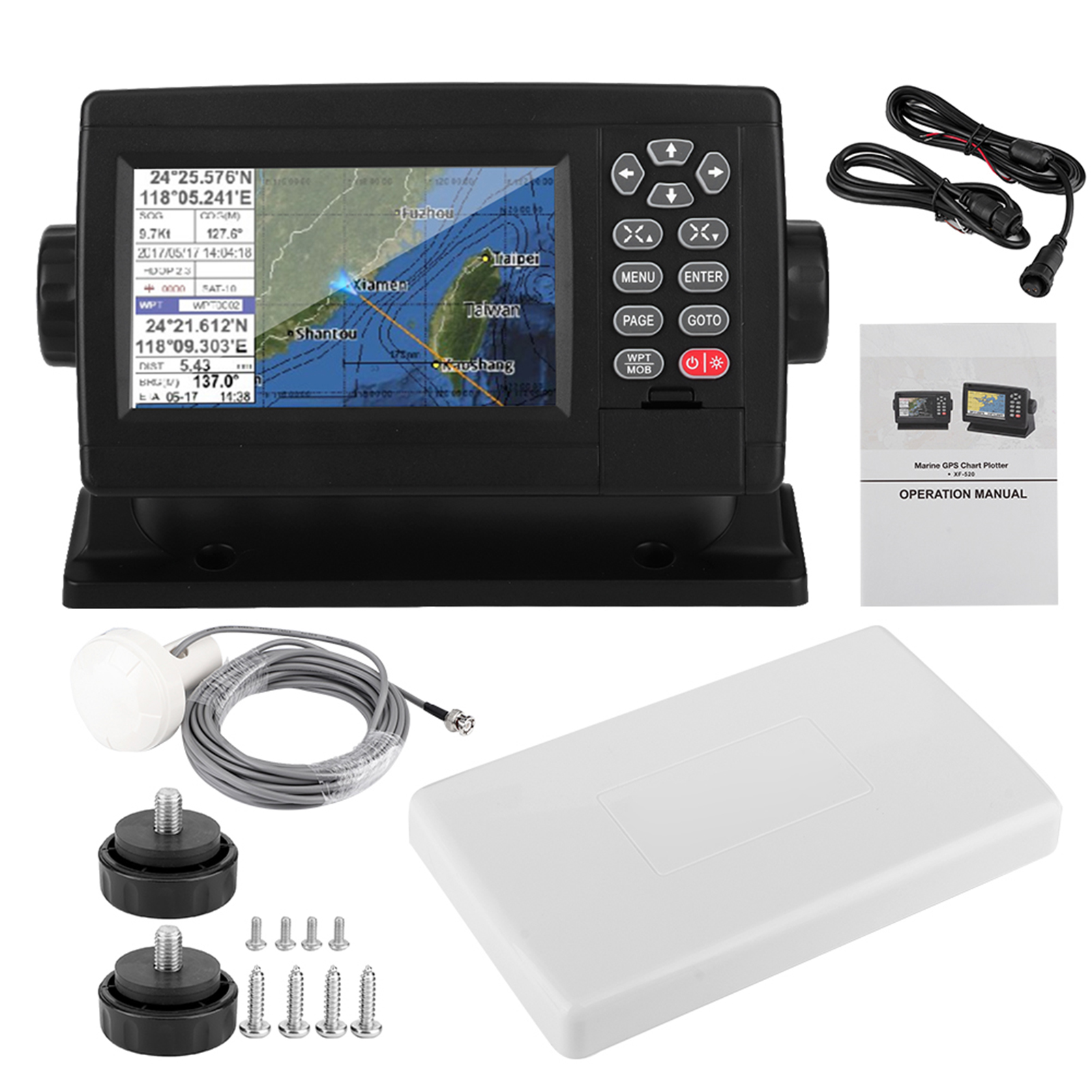 XF-520 5' Marine Satellite GPS Navigator Color LCD Display Dual-Mode Positioning Boat Chart Plotter GPS Navigation$525.00
XF-520 5' Marine Satellite GPS Navigator Color LCD Display Dual-Mode Positioning Boat Chart Plotter GPS Navigation$525.00 -
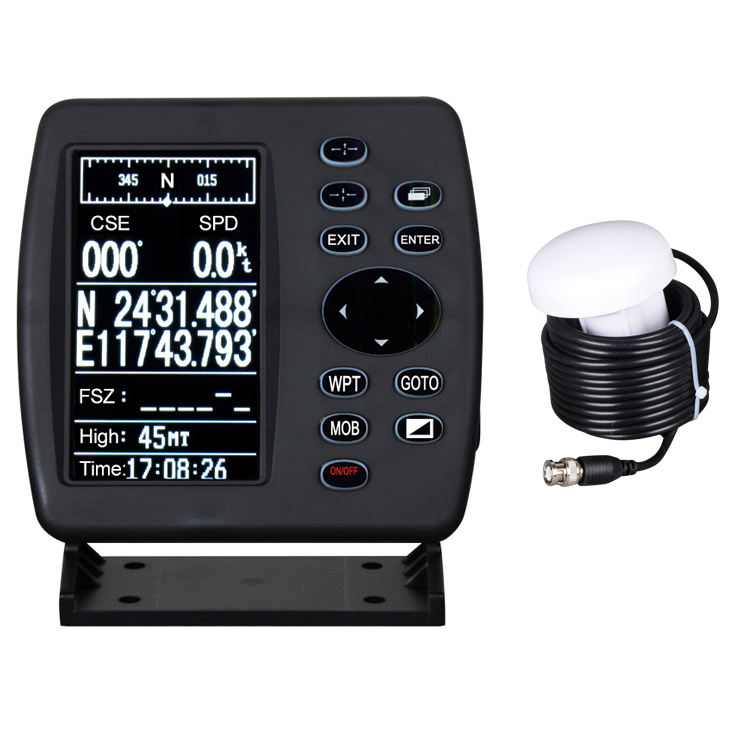 YSP-128 marine multi functional navigator GPS/AIS Chartplotter marine navigator NCS Multifunction Navigation fish finder$325.00
YSP-128 marine multi functional navigator GPS/AIS Chartplotter marine navigator NCS Multifunction Navigation fish finder$325.00 -
 KP-39 7inch ONWA marine GPS Chart plotter (with SD-card Map Chart sea) Chart Plotter Marine GPS Navigator$900.00
KP-39 7inch ONWA marine GPS Chart plotter (with SD-card Map Chart sea) Chart Plotter Marine GPS Navigator$900.00 -
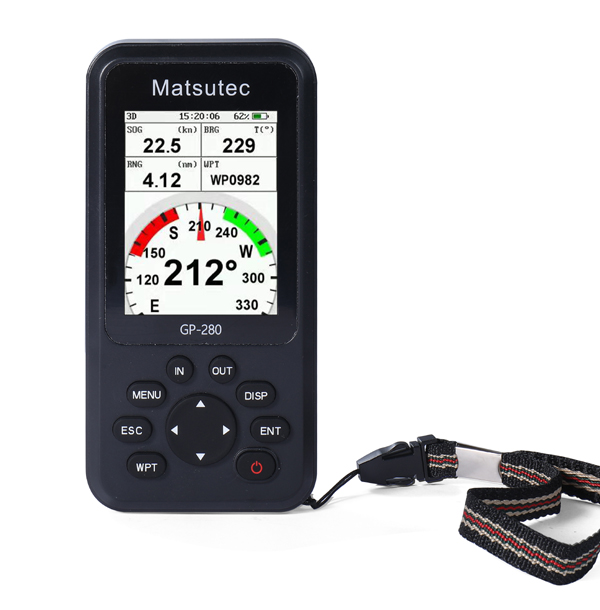 Matsutec GP-280 Marine GPS locator/Handheld GPS Navigator$900.00
Matsutec GP-280 Marine GPS locator/Handheld GPS Navigator$900.00 -
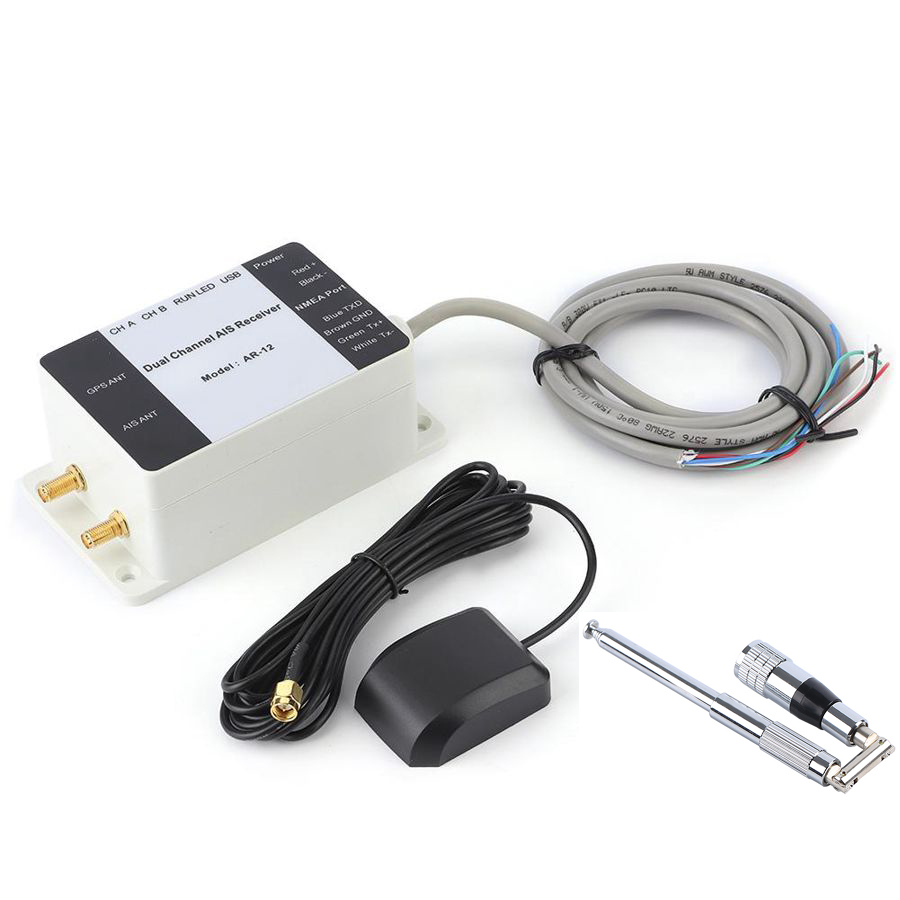 AR-12 Dual Channel AIS Receiver GPS USB Yacht Steamship NMEA Port Navigator Marine Boat$1200.00
AR-12 Dual Channel AIS Receiver GPS USB Yacht Steamship NMEA Port Navigator Marine Boat$1200.00 -
 ONWA KCombo-7 7inch Color LCD GPS plotter Combo with Fishfinder$6800.00
ONWA KCombo-7 7inch Color LCD GPS plotter Combo with Fishfinder$6800.00 -
 ONWA KP-708A 7-inch Color LCD GPS Chart Plotter with GPS Antenna and Built-in Class B AIS Transponder Combo Marine GPS Navigator$1200.00
ONWA KP-708A 7-inch Color LCD GPS Chart Plotter with GPS Antenna and Built-in Class B AIS Transponder Combo Marine GPS Navigator$1200.00 -
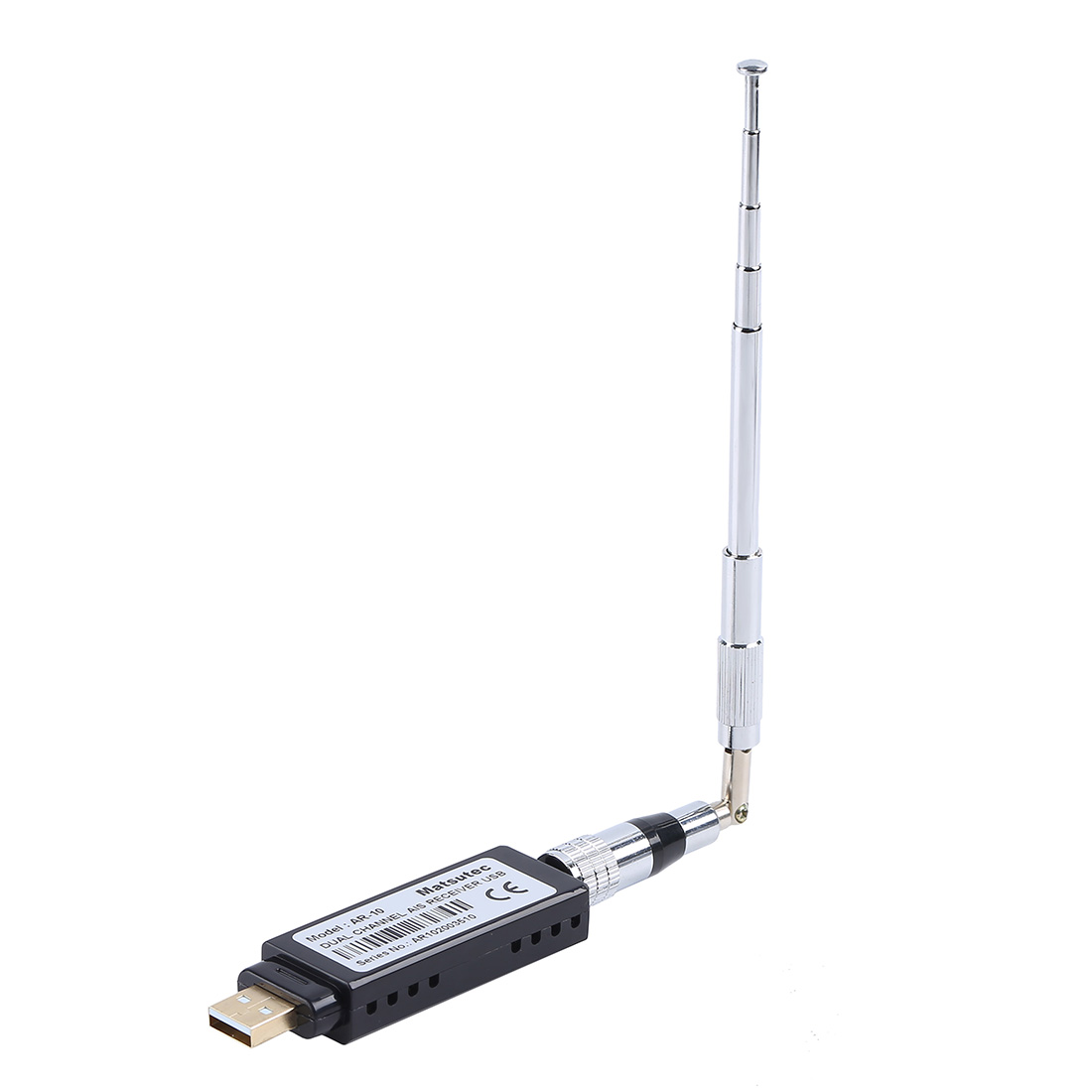 Matsutec AR-10 marine boat USB AIS Receiver$900.00
Matsutec AR-10 marine boat USB AIS Receiver$900.00 -
 ONWA KEC-30 marine Electronic Fluxgate compass$3500.00
ONWA KEC-30 marine Electronic Fluxgate compass$3500.00 -
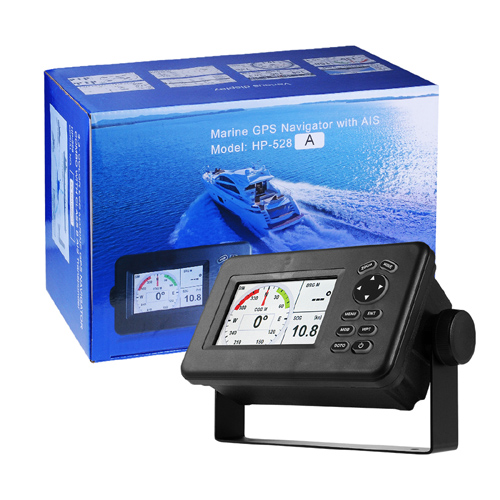 Matsutec HP-528A Class B AIS Transponder Marine GPS Navigator$5500.00
Matsutec HP-528A Class B AIS Transponder Marine GPS Navigator$5500.00 -
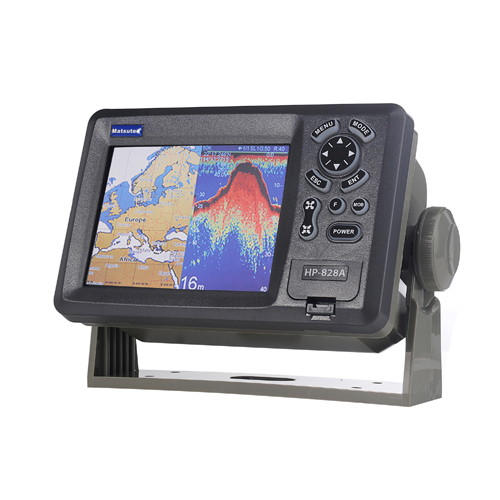 Matsutec HP-828A Class B AIS Transponder Marine GPS Navigator$7500.00
Matsutec HP-828A Class B AIS Transponder Marine GPS Navigator$7500.00 -
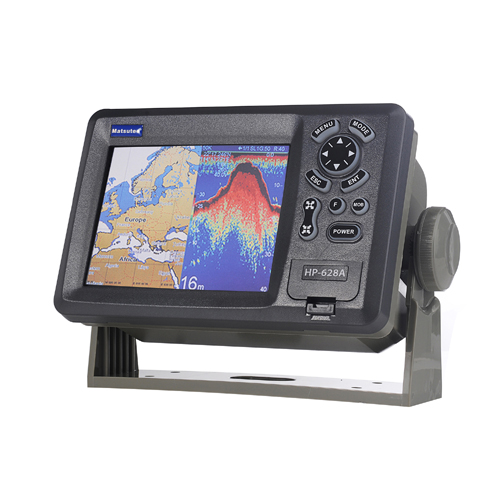 Matsutec HP-628A Class B AIS Transponder Marine GPS Navigator$6800.00
Matsutec HP-628A Class B AIS Transponder Marine GPS Navigator$6800.00
-
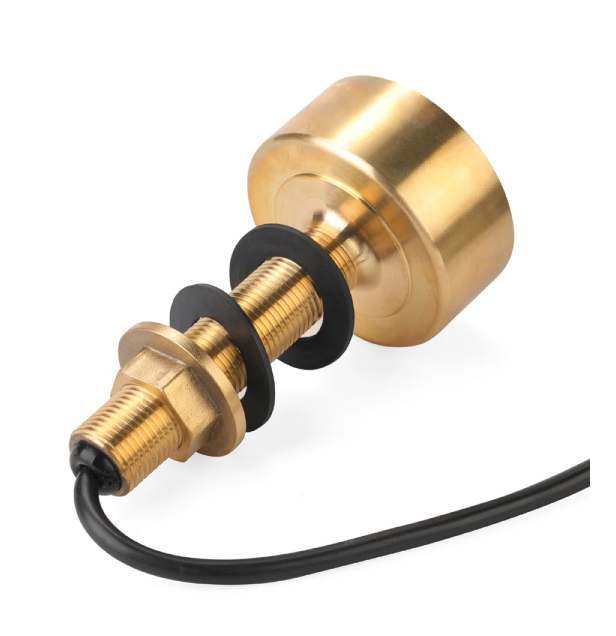 TD-25-10Pin TRANSDUCER FOR 10pin Fishing instrument dual frequency 600W520 5PSD 520 5MSD Depth Transducer$1500.00
TD-25-10Pin TRANSDUCER FOR 10pin Fishing instrument dual frequency 600W520 5PSD 520 5MSD Depth Transducer$1500.00 -
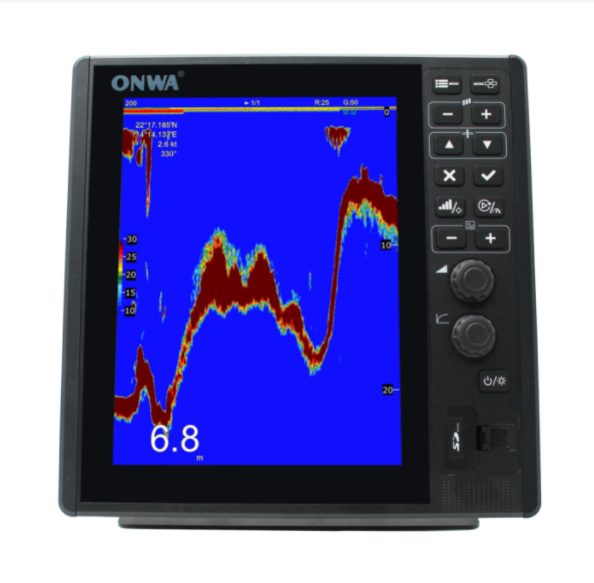 K-Fish-12 12 inch Dual Frequency Fish Finder ( Up to 2KW Power ) with 1kw or 2kw transducer$1200.00
K-Fish-12 12 inch Dual Frequency Fish Finder ( Up to 2KW Power ) with 1kw or 2kw transducer$1200.00 -
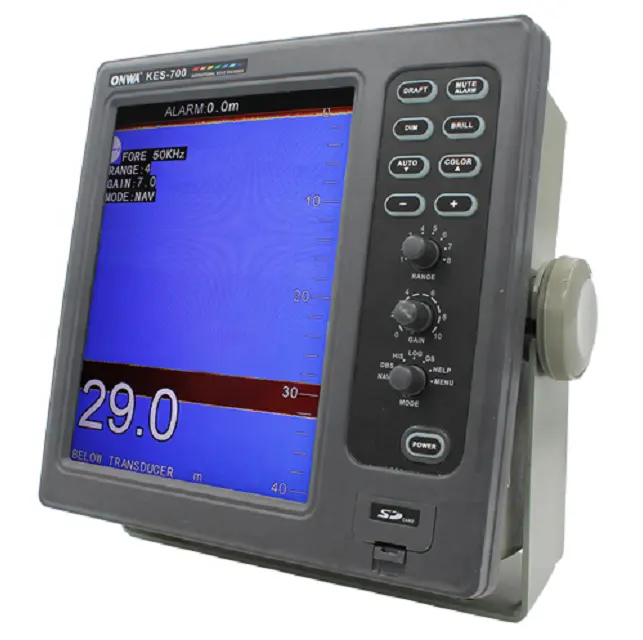 KES-700 10.4 inch Navigational Echo Sounder / fish finder /depth sounder with Memory Storage and Recall of Depth data$2000.00
KES-700 10.4 inch Navigational Echo Sounder / fish finder /depth sounder with Memory Storage and Recall of Depth data$2000.00 -
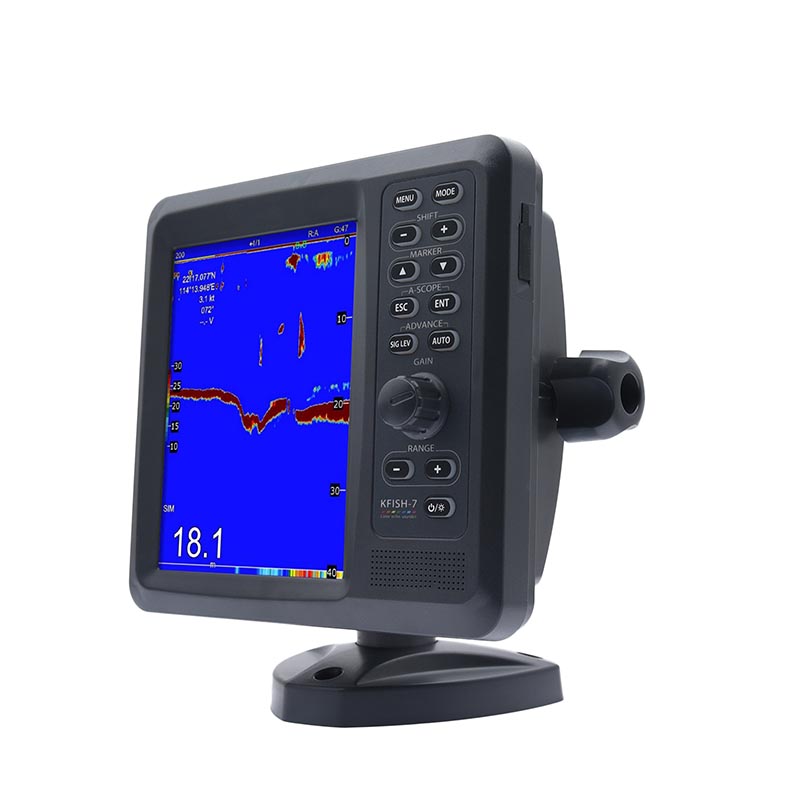 KFISH -7 Marine fish Finder depth sounder sonar fish finder With Dual Frequency,with TRANSDUCERS$900.00
KFISH -7 Marine fish Finder depth sounder sonar fish finder With Dual Frequency,with TRANSDUCERS$900.00 -
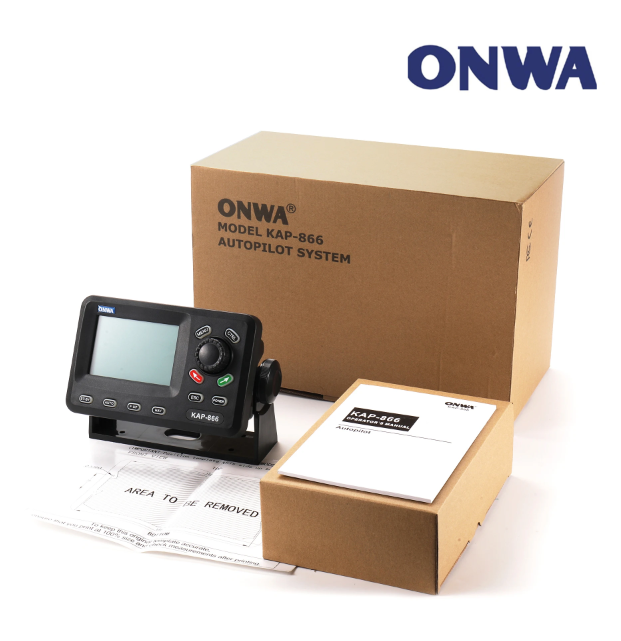 ONWA KAP-866 autopilot system Remote Control 4.5-inch Marine Autopilot System (Auto Pilot)$7500.00
ONWA KAP-866 autopilot system Remote Control 4.5-inch Marine Autopilot System (Auto Pilot)$7500.00 -
 Matsutec HP-528 Marine GPS /SBAS navigator$600.00
Matsutec HP-528 Marine GPS /SBAS navigator$600.00 -
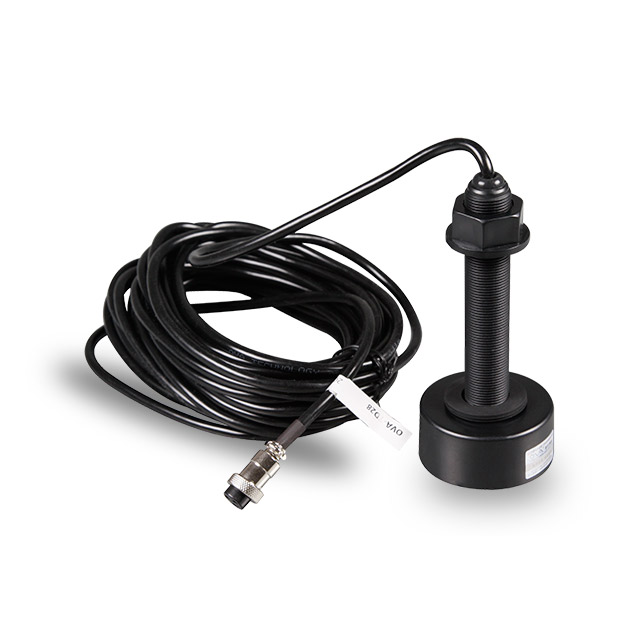 Matsutec TD-28 200KHz Ultrasonic Fish Finder Transducer$1200.00
Matsutec TD-28 200KHz Ultrasonic Fish Finder Transducer$1200.00 -
 Matsutec HF-620 MARINE COLOR ECHO SOUNDER Fishfinder$7000.00
Matsutec HF-620 MARINE COLOR ECHO SOUNDER Fishfinder$7000.00 -
 Matsutec MS-105 VHF Marine Radio Transceiver IP-67$390.00
Matsutec MS-105 VHF Marine Radio Transceiver IP-67$390.00 -
 Matsutec HAB-130 Marine Boat Fishing boat Positioning apparatus AIS Fishing Net with Antenna IPX7 GPS Anti-lost Tracker Locator$690.00
Matsutec HAB-130 Marine Boat Fishing boat Positioning apparatus AIS Fishing Net with Antenna IPX7 GPS Anti-lost Tracker Locator$690.00
-
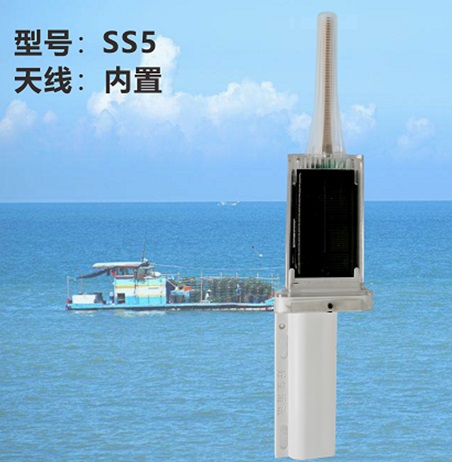 Matsuec HAB-140 Solar Charge AIS Buoy SS5$300.00
Matsuec HAB-140 Solar Charge AIS Buoy SS5$300.00 -
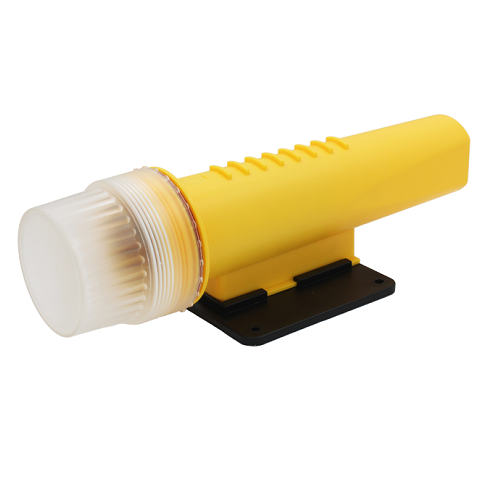 Matsutec Marine AIS Beacon KS-33NT$300.00
Matsutec Marine AIS Beacon KS-33NT$300.00 -
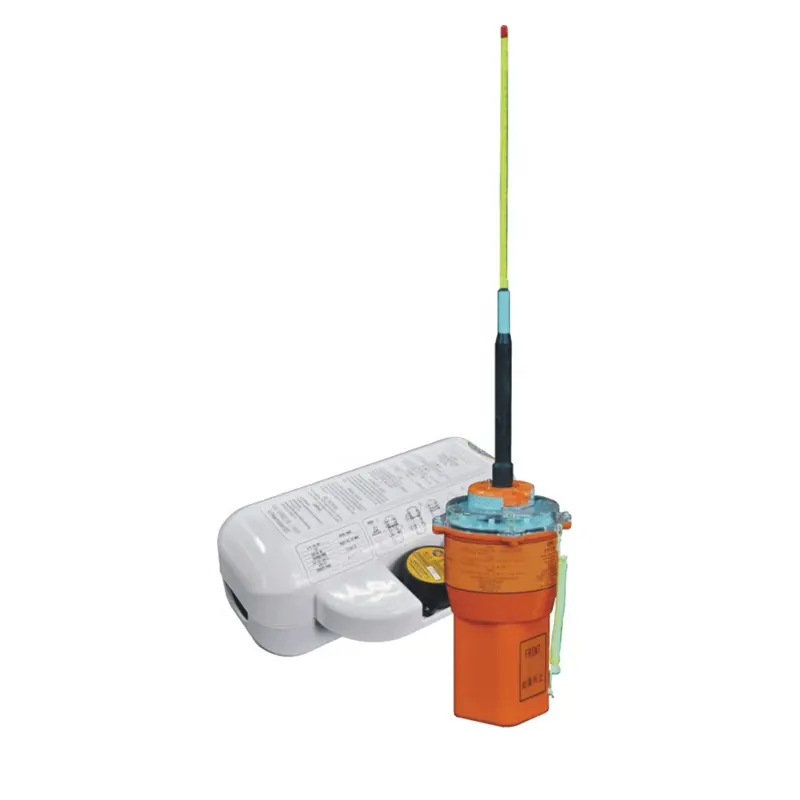 VEP8 shipboard satellite emergency position indicator EPIRB maritime distress emergency search and rescue position indicator$700.00
VEP8 shipboard satellite emergency position indicator EPIRB maritime distress emergency search and rescue position indicator$700.00 -
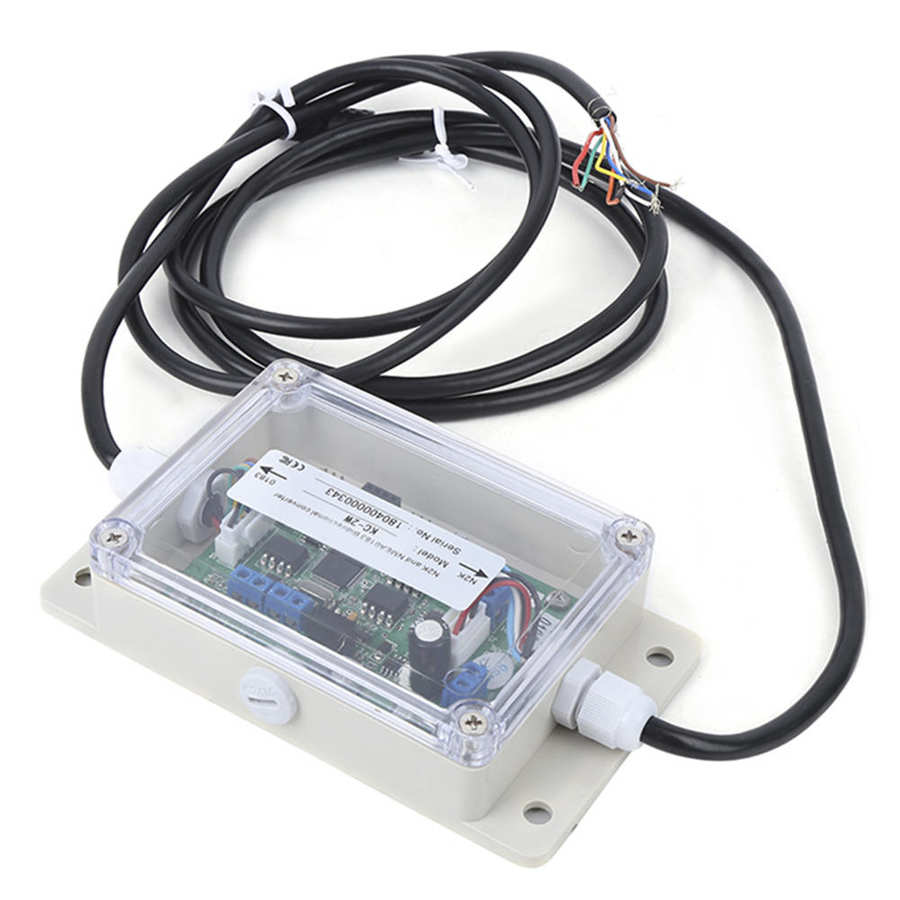 KC-2W NMEA2000 And NMEA0183 Bidirection Converter NMEA0183 to N2K converter KC-2W WIFI module$195.00
KC-2W NMEA2000 And NMEA0183 Bidirection Converter NMEA0183 to N2K converter KC-2W WIFI module$195.00 -
 Matsutec HAB-150S A/S Fishing Net Tracking Buoy+SOS Button$2500.00
Matsutec HAB-150S A/S Fishing Net Tracking Buoy+SOS Button$2500.00 -
 Matsutec HAB-150 Small Boat AIS Fishing Net Tracking Buoy$2500.00
Matsutec HAB-150 Small Boat AIS Fishing Net Tracking Buoy$2500.00 -
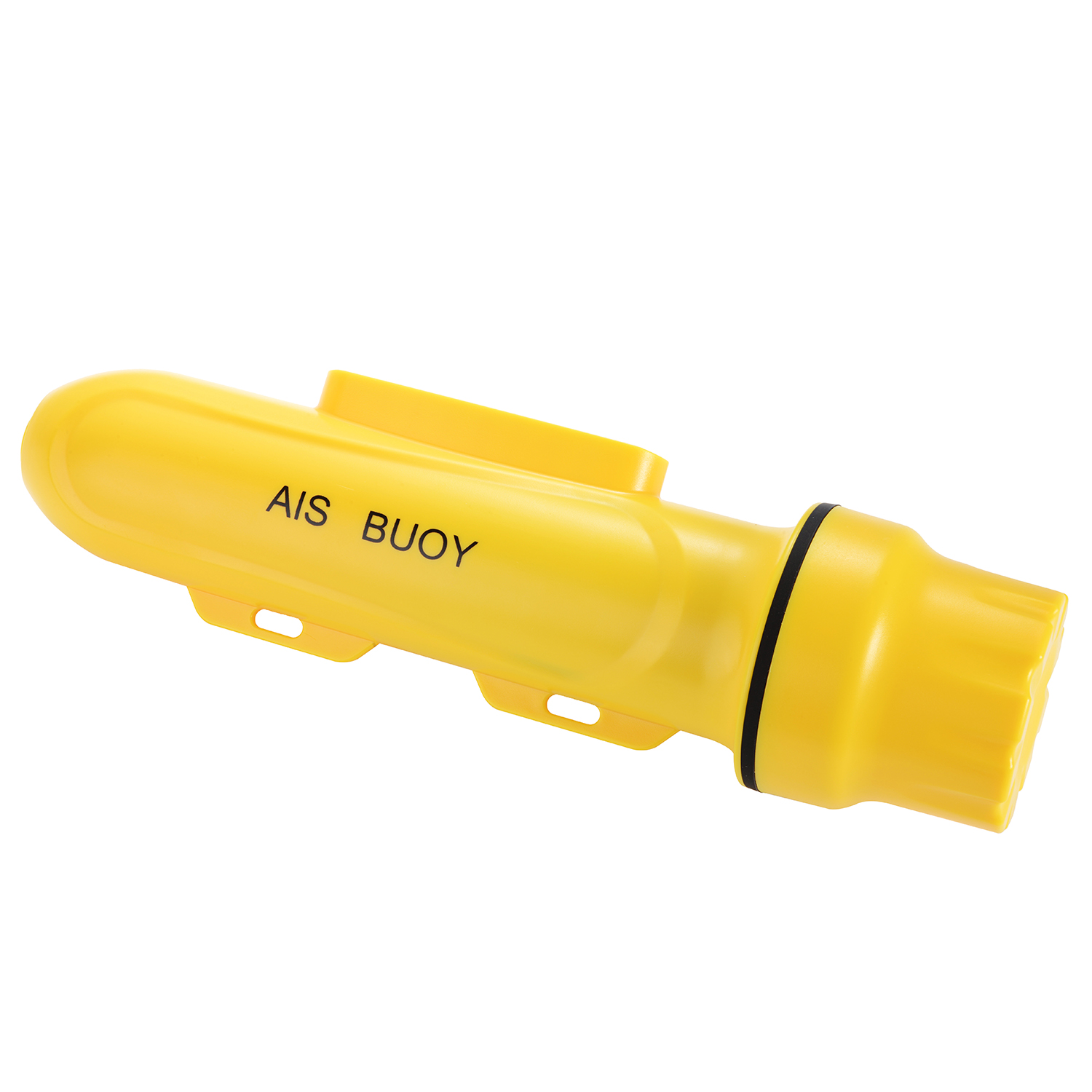 Matsutec HAB-120 A/S Fishing Net Tracking Buoy$1950.00
Matsutec HAB-120 A/S Fishing Net Tracking Buoy$1950.00 -
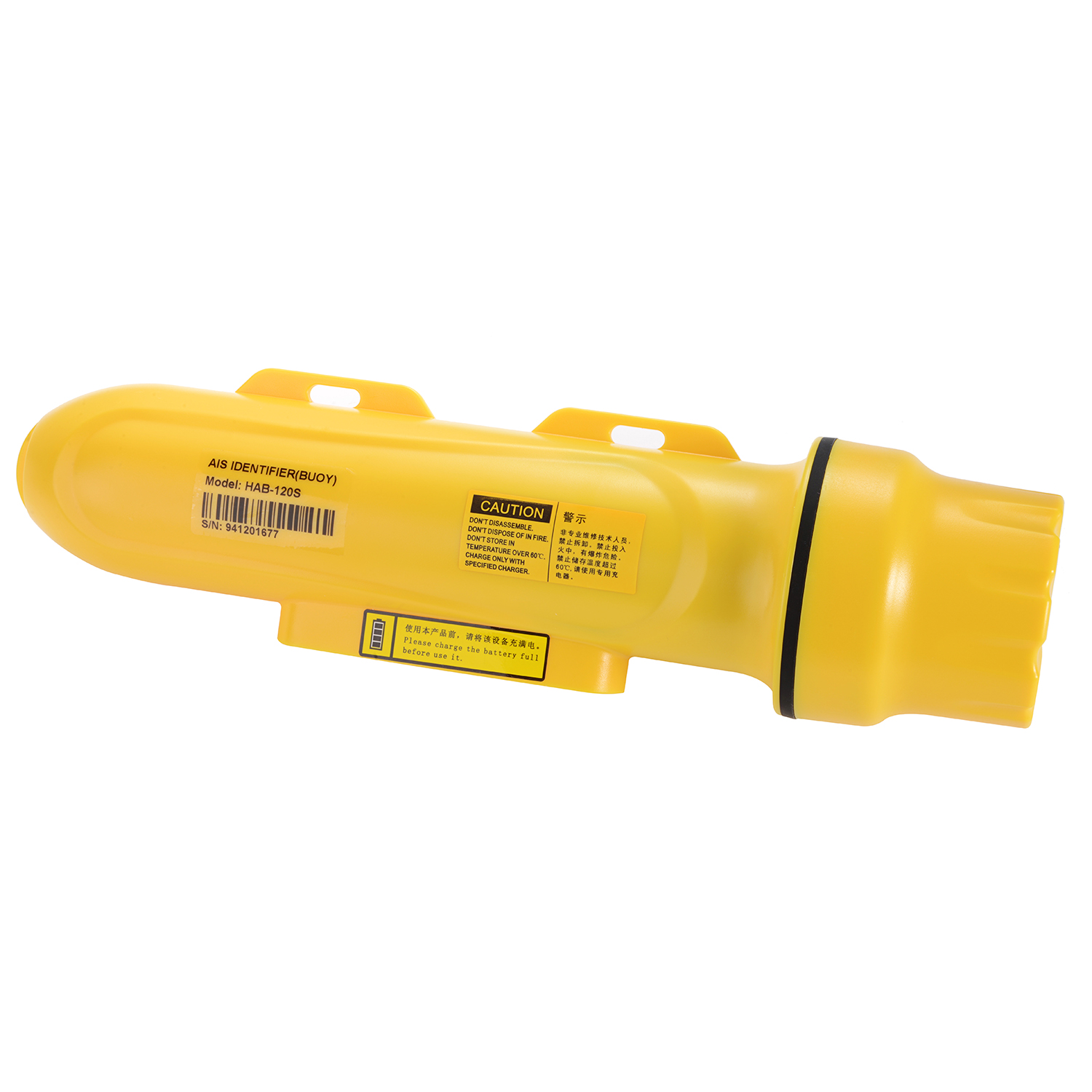 Matsutec HAB-120S A/S Fishing Net Tracking Buoy+SOS Button$2100.00
Matsutec HAB-120S A/S Fishing Net Tracking Buoy+SOS Button$2100.00 -
 Matsutec HY-AIS-1.2M Antenna$1300.00
Matsutec HY-AIS-1.2M Antenna$1300.00 -
 Matsutec HY-DSC-1.2M Antenna$1300.00
Matsutec HY-DSC-1.2M Antenna$1300.00
-
 Matsutec HA-021 Boat Ship Marine GPS and Glonass Antenna receiver dual band Navigation External Antenna (5m Cable) Compatible$50.00
Matsutec HA-021 Boat Ship Marine GPS and Glonass Antenna receiver dual band Navigation External Antenna (5m Cable) Compatible$50.00 -
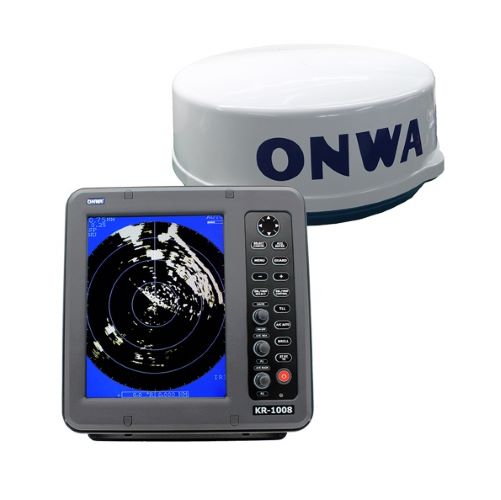 Matsutec ONWA 10.4 inch Marine Radar KR-1008/ KR-1068$3000.00
Matsutec ONWA 10.4 inch Marine Radar KR-1008/ KR-1068$3000.00 -
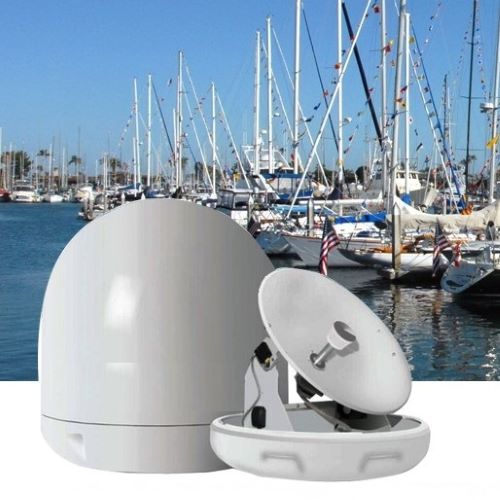 Matsutec Marine Automatic Tracking Satellite TVRO Antenna$3000.00
Matsutec Marine Automatic Tracking Satellite TVRO Antenna$3000.00 -
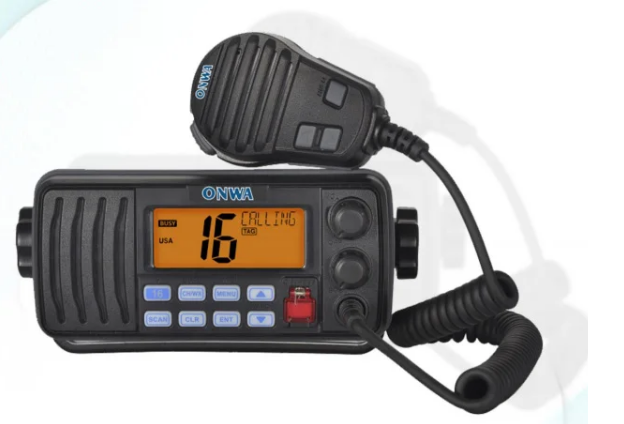 KV-290 VHF/DSC marine Radio Transceiver with built-in Class D$300.00
KV-290 VHF/DSC marine Radio Transceiver with built-in Class D$300.00 -
 KP-1299 12.1-inch GPS Chart Plotter (Expandable Features) GPS Chart Plotter$2200.00
KP-1299 12.1-inch GPS Chart Plotter (Expandable Features) GPS Chart Plotter$2200.00 -
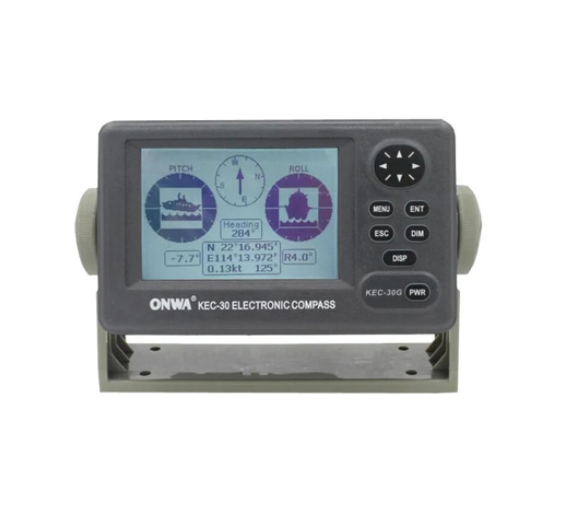 KEC-30G(MK2) ONWA Electronic Fluxgate compass with GPS / KEC-30G Electronic GPS compass with Hemisphere V104S GPS Compass$750.00
KEC-30G(MK2) ONWA Electronic Fluxgate compass with GPS / KEC-30G Electronic GPS compass with Hemisphere V104S GPS Compass$750.00 -
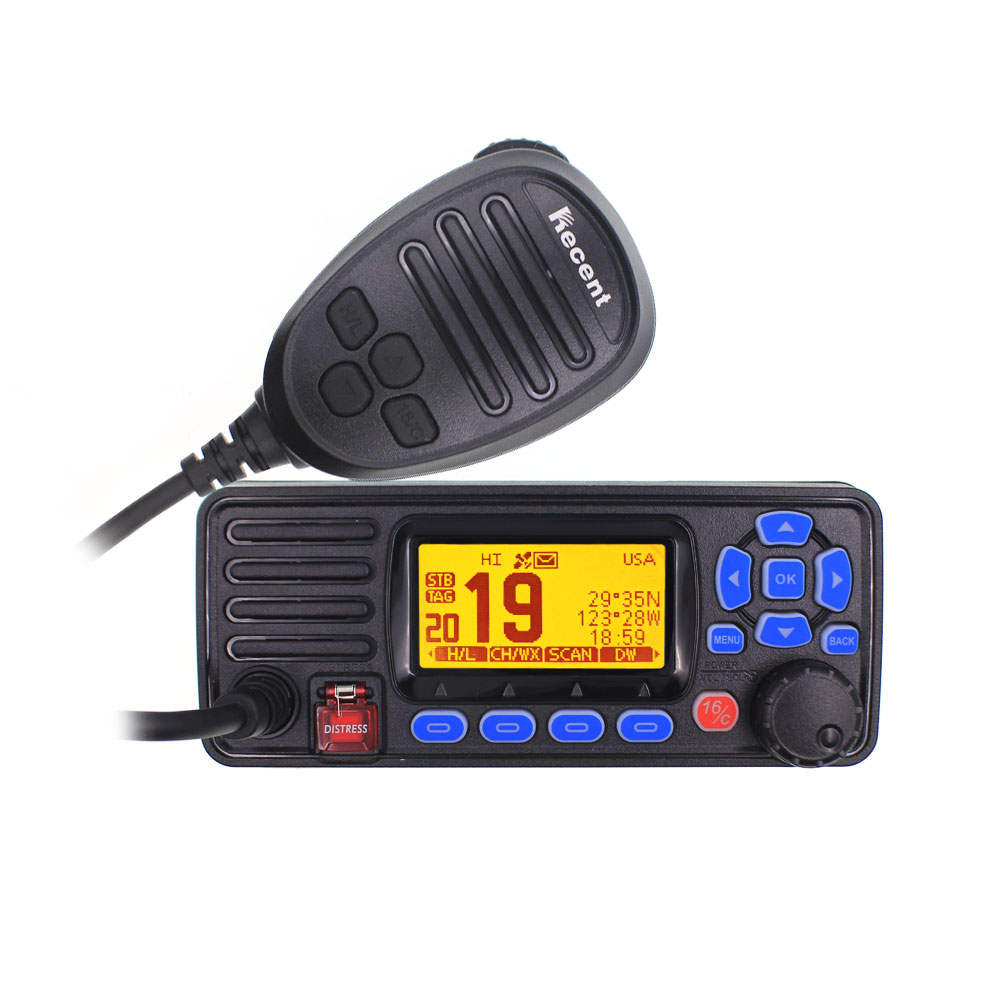 Walkie Talkie RS-509MG Built-in GPS Positioning VHF Marine Transceiver IPX7 Waterproof 25W Marine Radio DSC$225.00
Walkie Talkie RS-509MG Built-in GPS Positioning VHF Marine Transceiver IPX7 Waterproof 25W Marine Radio DSC$225.00 -
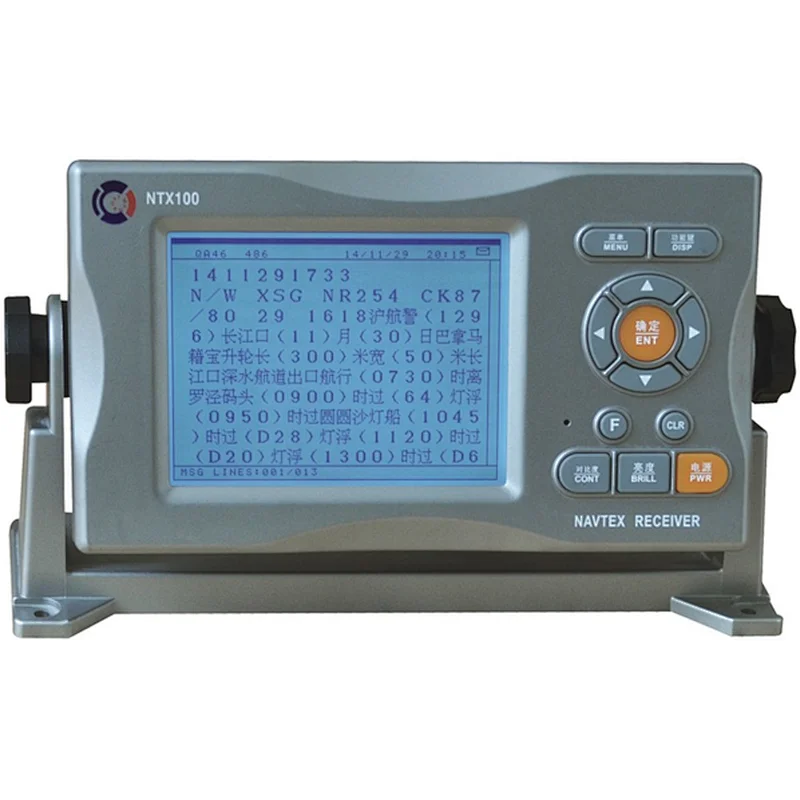 Navtex receiver navigational telex NTX-100 CY GMDSS life saving solas IMO ship electronics navigation communication$700.00
Navtex receiver navigational telex NTX-100 CY GMDSS life saving solas IMO ship electronics navigation communication$700.00 -
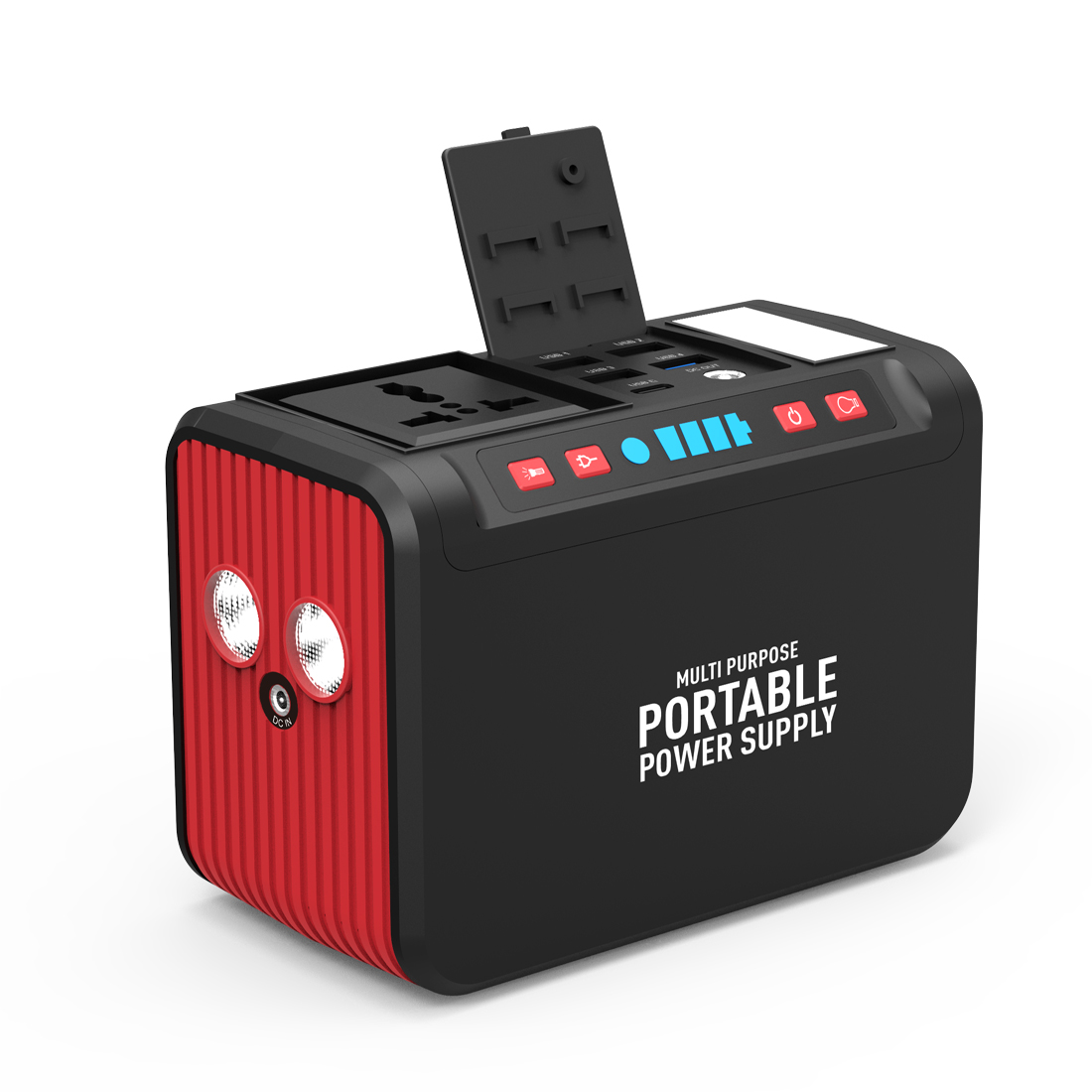 Matsutec S81 Power Source 74WH$2300.00
Matsutec S81 Power Source 74WH$2300.00 -
 Matsutec Air Radio Antenna 118MHZ-139MHZ$950.00
Matsutec Air Radio Antenna 118MHZ-139MHZ$950.00 -
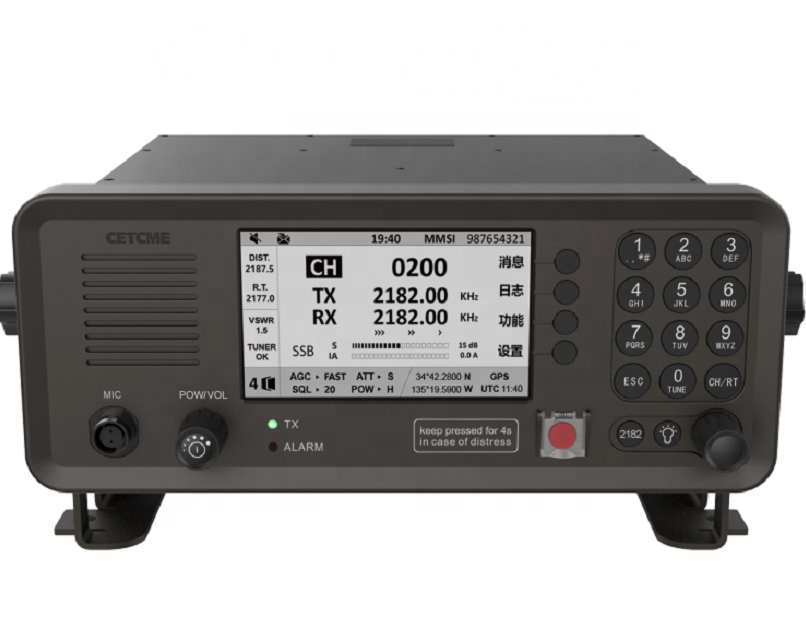 WT-6000 MF/HF Transceiver With antenna coupler$4300.00
WT-6000 MF/HF Transceiver With antenna coupler$4300.00 -
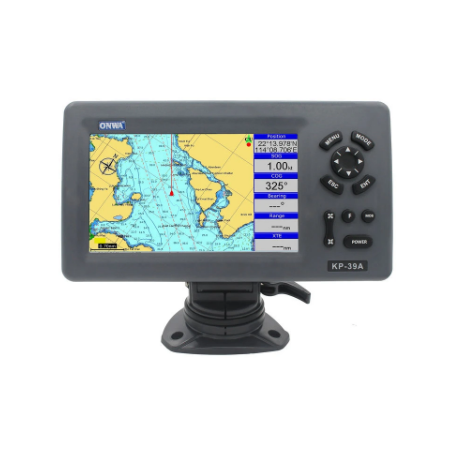 KP-39A 7-inch Color LCD GPS Chart Plotter with GPS Antenna and Built-in Class B AIS Transponder Combo Marine GPS Navigator$2200.00
KP-39A 7-inch Color LCD GPS Chart Plotter with GPS Antenna and Built-in Class B AIS Transponder Combo Marine GPS Navigator$2200.00 -
 Matsutec ISD-190 Docking Station For Inmarsat Isatphone Pro$2900.00
Matsutec ISD-190 Docking Station For Inmarsat Isatphone Pro$2900.00 -
 Matsutec FDU-XT Docking Station For Thuraya XT$3900.00
Matsutec FDU-XT Docking Station For Thuraya XT$3900.00 -
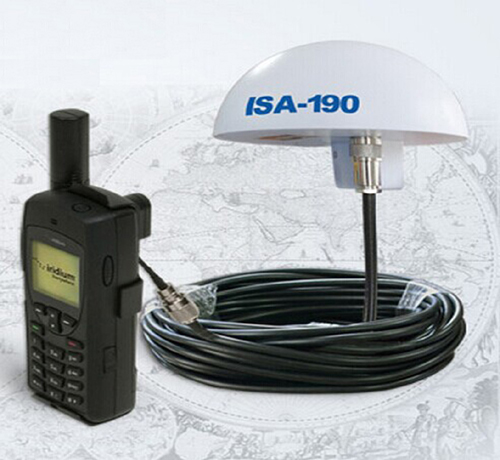 Matsutec ISA-190B Satellite Antenna ISA-190B for IRIDIUM 9555/9575$2300.00
Matsutec ISA-190B Satellite Antenna ISA-190B for IRIDIUM 9555/9575$2300.00 -
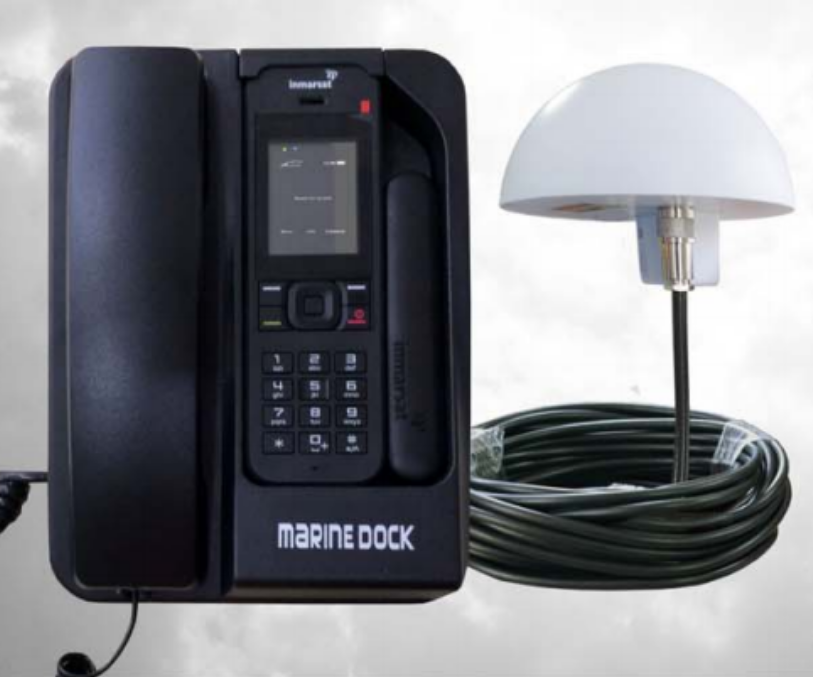 Matsutec Isatdock 2 Docking Station For Inmarsat Isatphone 2$3500.00
Matsutec Isatdock 2 Docking Station For Inmarsat Isatphone 2$3500.00 -
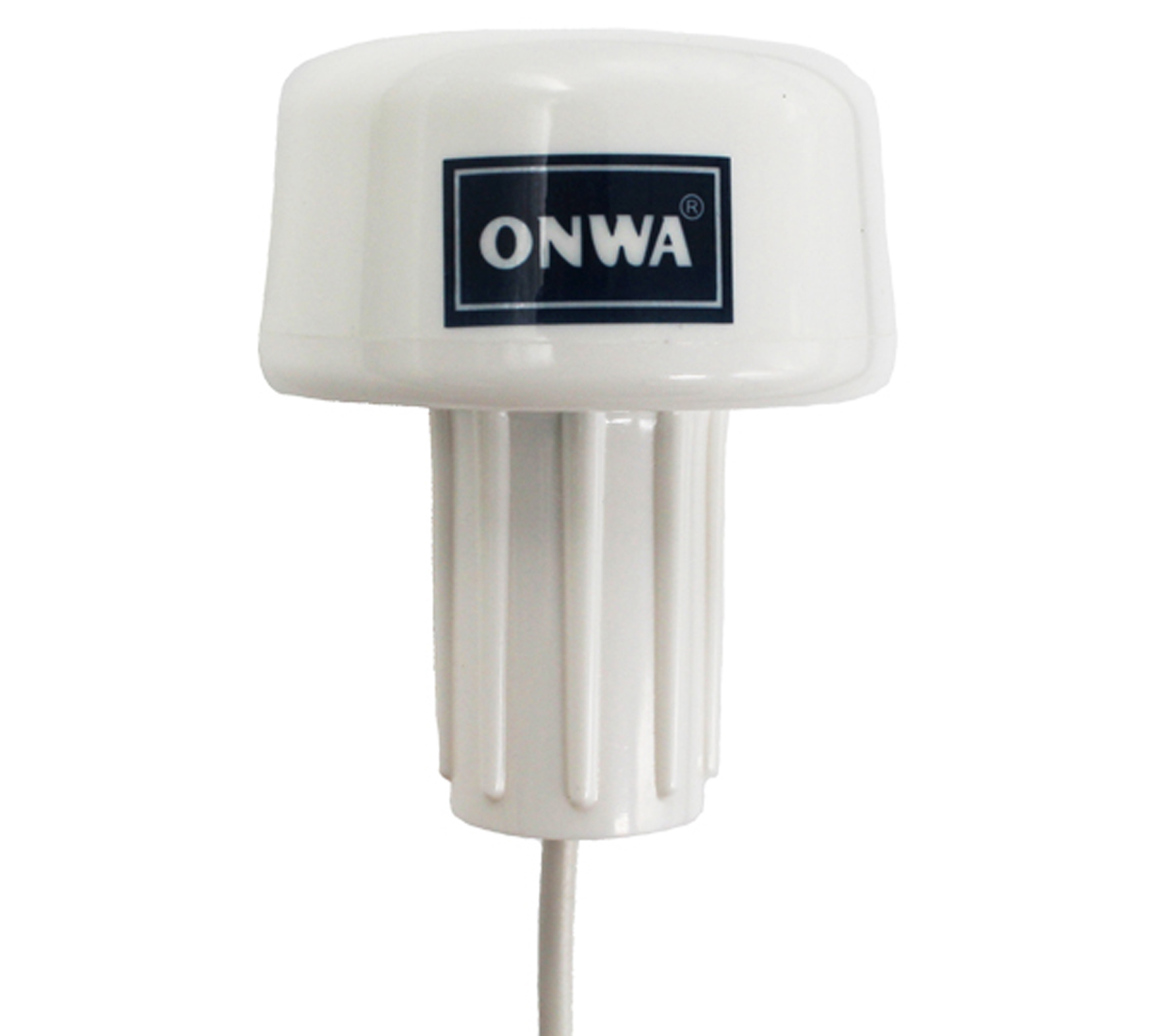 ONWA KA-GC9A 9-Axis Electronic Compass with Built-in High Accuracy GPS Module$330.00
ONWA KA-GC9A 9-Axis Electronic Compass with Built-in High Accuracy GPS Module$330.00
-
 Matsutec NPC-150 ais pilot plug wifi electronic chart pilot interface to wireless adapter for marine rs485 device$200.00
Matsutec NPC-150 ais pilot plug wifi electronic chart pilot interface to wireless adapter for marine rs485 device$200.00 -
 Matsutec XA-201 Class B Automatic Identification System$6000.00
Matsutec XA-201 Class B Automatic Identification System$6000.00 -
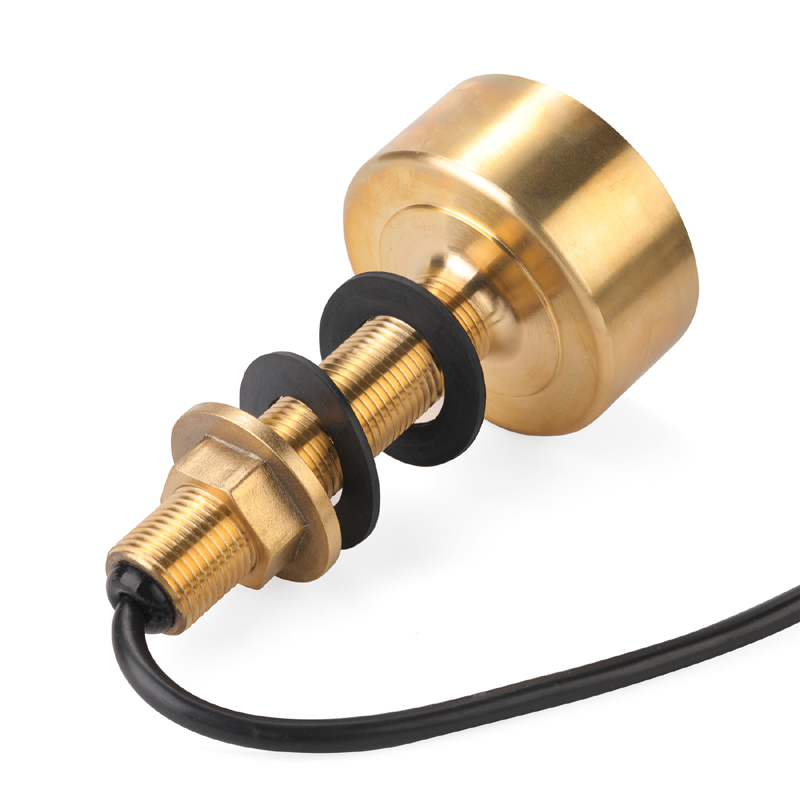 Matsutec TD-25 with Cable 10M Sonar Small Waterproof Transducer 600W 50&200KHz Thru Hull Bronze Depth Transducer$300.00
Matsutec TD-25 with Cable 10M Sonar Small Waterproof Transducer 600W 50&200KHz Thru Hull Bronze Depth Transducer$300.00 -
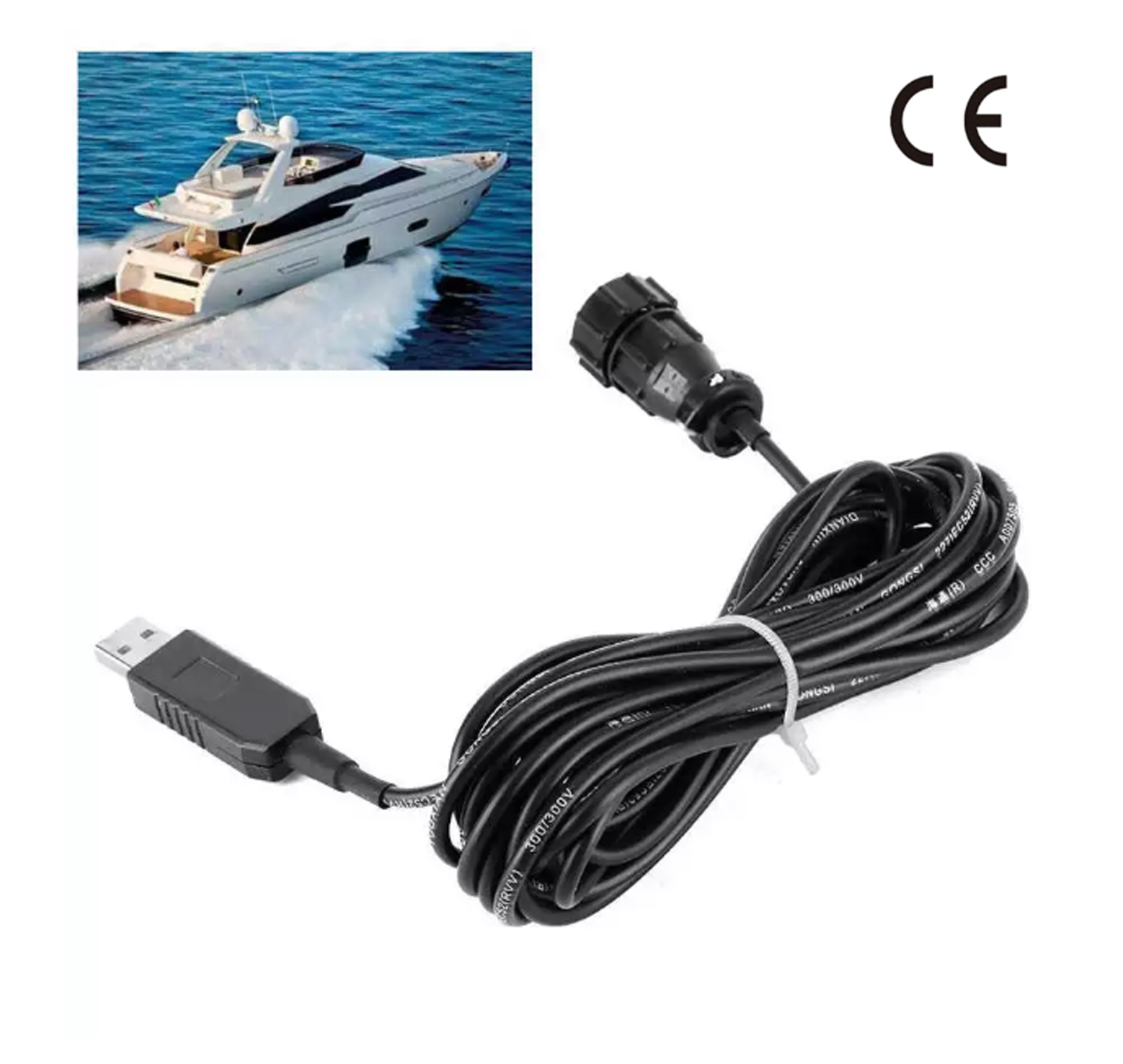 NPC-100 AIS Pilot Plug USB data cable 2 Meter IMO Standard AIS Pilot Plug interfaces USB 2.0 cable$111.00
NPC-100 AIS Pilot Plug USB data cable 2 Meter IMO Standard AIS Pilot Plug interfaces USB 2.0 cable$111.00 -
 AIS TRANSPONDER MA-110 (Standard) Class A$3500.00
AIS TRANSPONDER MA-110 (Standard) Class A$3500.00 -
 AIS TRANSPONDER MA-110 (Advanced) Class A$4000.00
AIS TRANSPONDER MA-110 (Advanced) Class A$4000.00 -
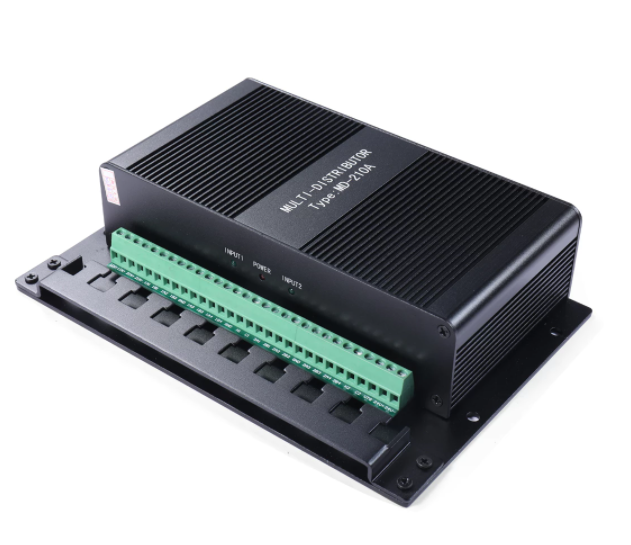 MD-210 NMEA marine signal splitter marine NMEA Distributor$1700.00
MD-210 NMEA marine signal splitter marine NMEA Distributor$1700.00 -
 Matsutec GC-2000 Gyro Converter NMEA0183 Digital with display$2200.00
Matsutec GC-2000 Gyro Converter NMEA0183 Digital with display$2200.00 -
 Matsutec SPAT-1030A AIS SART for distress boat$2900.00
Matsutec SPAT-1030A AIS SART for distress boat$2900.00 -
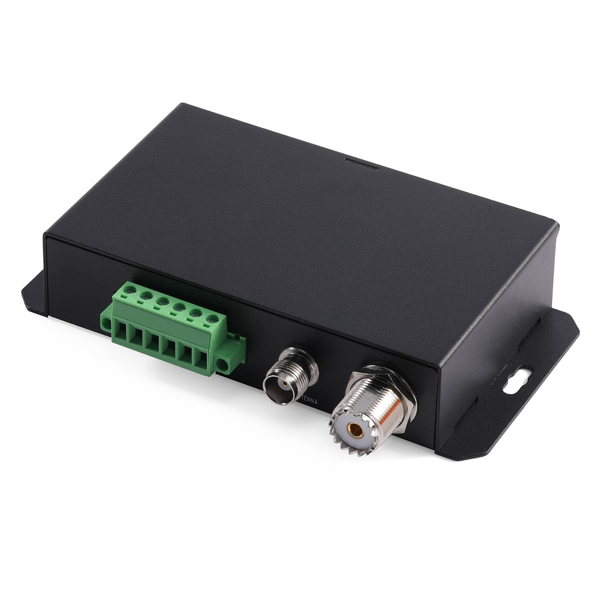 Matsutec HAR-100 Dual Channel AIS Receiver With RS232/ RS422 , GPS receiver$3000.00
Matsutec HAR-100 Dual Channel AIS Receiver With RS232/ RS422 , GPS receiver$3000.00 -
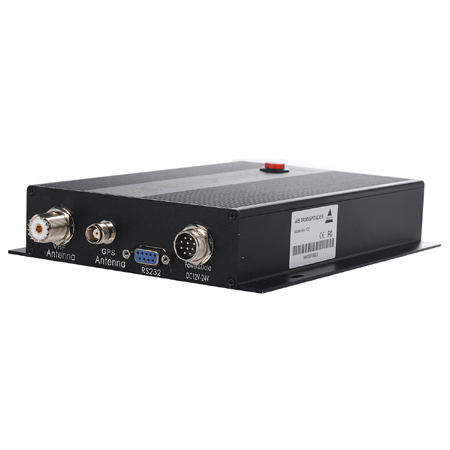 Matsutec HA-102 Marine AIS receiver and transmitter$2500.00
Matsutec HA-102 Marine AIS receiver and transmitter$2500.00 -
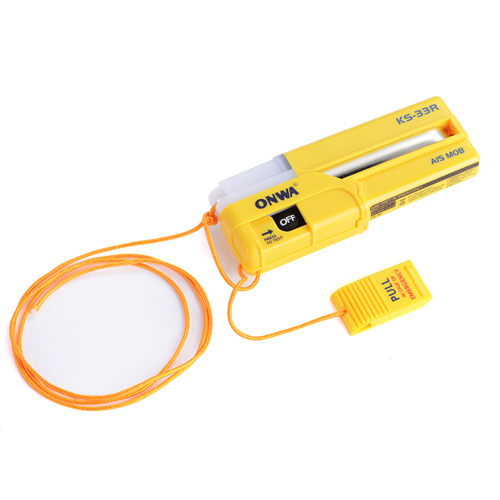 ONWA KS-33R AIS-MOB Personal locator beacon tracker Smartfind AIS MOB$2200.00
ONWA KS-33R AIS-MOB Personal locator beacon tracker Smartfind AIS MOB$2200.00
-
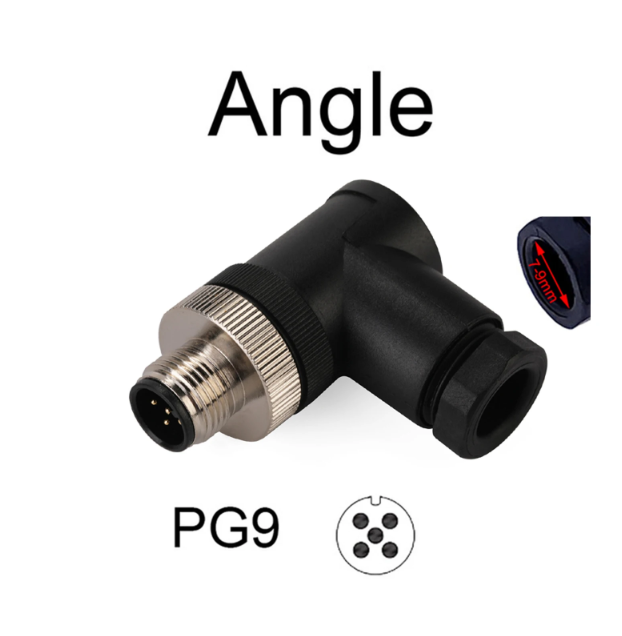 NMEA 2000 5Pin Angle Male PG9 For NMEA 2000 N2K Male Termination Resistor M12 5 Pin IP67 Waterproof for Lowrance Navico Garmin$12.00
NMEA 2000 5Pin Angle Male PG9 For NMEA 2000 N2K Male Termination Resistor M12 5 Pin IP67 Waterproof for Lowrance Navico Garmin$12.00 -
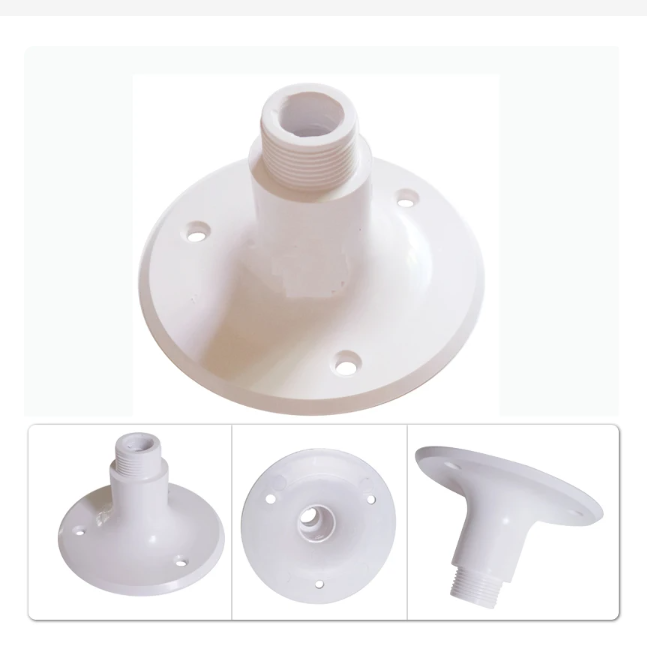 Matsutec Marine VHF GPS Antenna Mounts MARINE Boat Fixed Mount Antenna Base Injection Molded Nylon White$10.00
Matsutec Marine VHF GPS Antenna Mounts MARINE Boat Fixed Mount Antenna Base Injection Molded Nylon White$10.00 -
 NMEA 2000 5Pin Straight Male PG9 connector waterproof male&female plug screw threaded coupling 5 Pin A type sensor connectors$10.00
NMEA 2000 5Pin Straight Male PG9 connector waterproof male&female plug screw threaded coupling 5 Pin A type sensor connectors$10.00 -
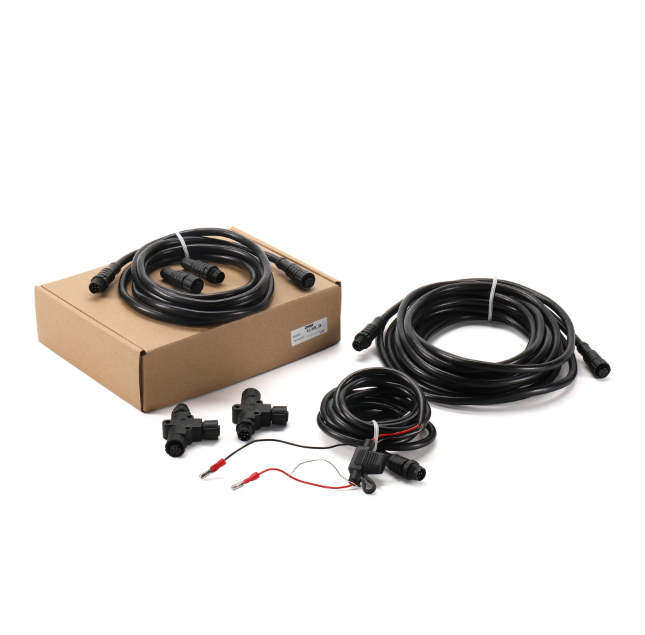 Matsutec KC-N2K_SK: N2K (NMEA2000) Starter kit NMEA 2000 N2K Termination Resistor M12 5Pin for Lowrance Navico Garmin$200.00
Matsutec KC-N2K_SK: N2K (NMEA2000) Starter kit NMEA 2000 N2K Termination Resistor M12 5Pin for Lowrance Navico Garmin$200.00 -
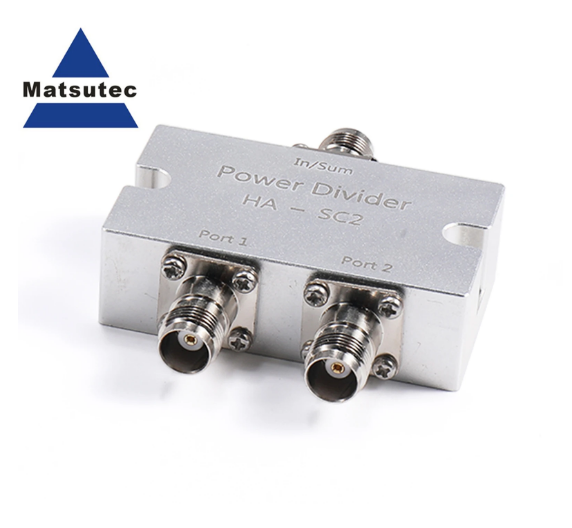 Matsutec HA-SC2 GPS Glonass Antenna Splitter GPS Antenna Splitter / GPS Antenna Power Splitter/Combiner TNC or BNC Port$50.00
Matsutec HA-SC2 GPS Glonass Antenna Splitter GPS Antenna Splitter / GPS Antenna Power Splitter/Combiner TNC or BNC Port$50.00 -
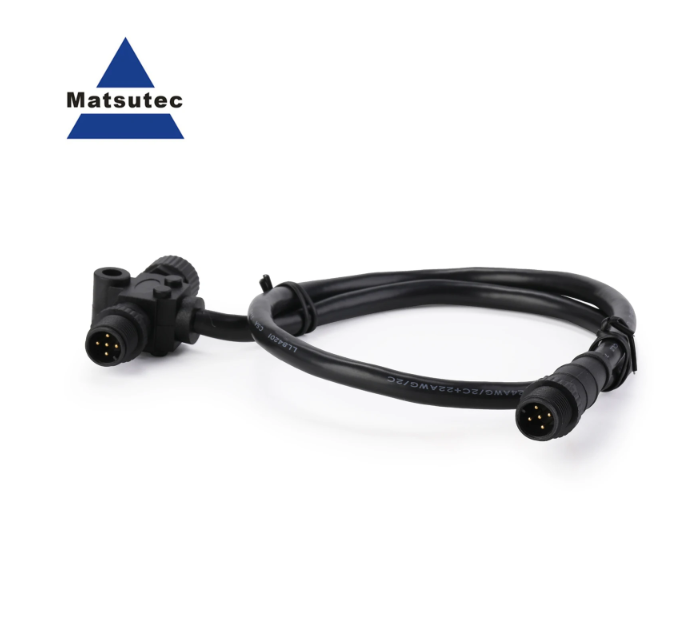 Matsutec NMEA 2000 (N2k) Marine Grade Products T-Connector Tee Power Cable with Fuse for Lowrance Navico Garmin Networks(1.65ft)$30.00
Matsutec NMEA 2000 (N2k) Marine Grade Products T-Connector Tee Power Cable with Fuse for Lowrance Navico Garmin Networks(1.65ft)$30.00 -
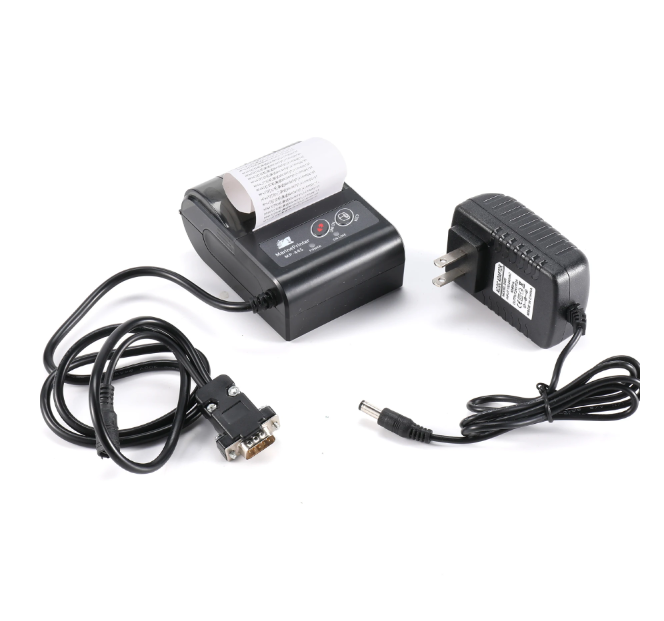 MP445 printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor GMDSS NAVTEX RECEIVER THERMAL PRINTER$200.00
MP445 printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor GMDSS NAVTEX RECEIVER THERMAL PRINTER$200.00 -
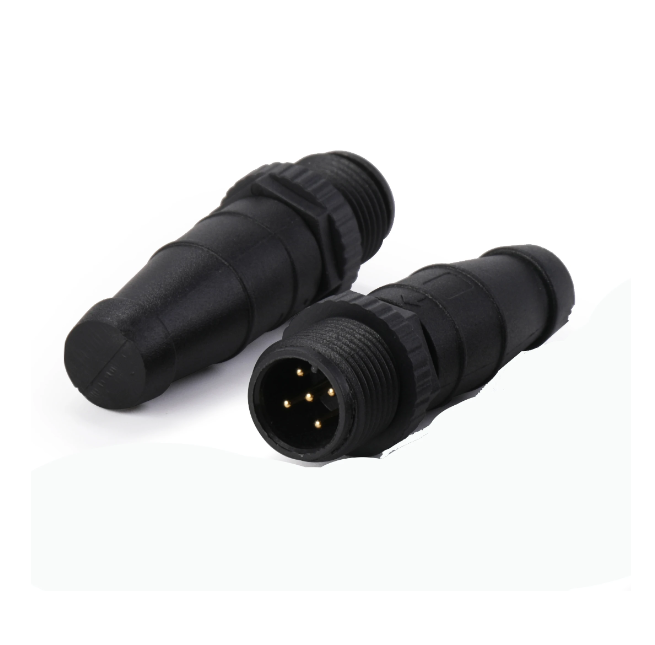 Matsutec NMEA 2000 (N2k) Starter kit 5pin Micro Male Termin Terminator Connector Resistance Connector Adapter Male Female Resistance$25.00
Matsutec NMEA 2000 (N2k) Starter kit 5pin Micro Male Termin Terminator Connector Resistance Connector Adapter Male Female Resistance$25.00 -
 Marine VHF Antenna Mounts, Adjustable Base VHF Antenna Mount for Boat, 316 Stainless Steel, Include Installation Screws$35.00
Marine VHF Antenna Mounts, Adjustable Base VHF Antenna Mount for Boat, 316 Stainless Steel, Include Installation Screws$35.00 -
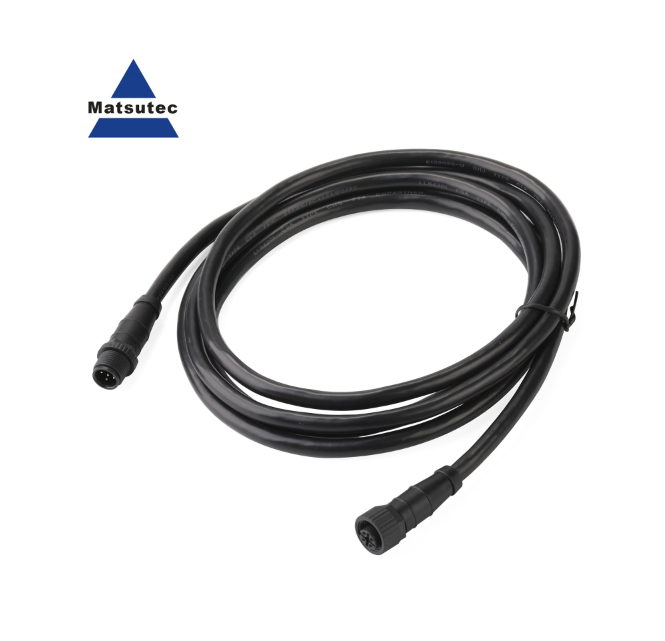 Matsutec M12 5pin NMEA 2000 (N2K) Starter kit 1/2meter 4, 5meter Backbone or Drop, Cable for Lowrance Simrad B&G Navico & Garmin$30.00
Matsutec M12 5pin NMEA 2000 (N2K) Starter kit 1/2meter 4, 5meter Backbone or Drop, Cable for Lowrance Simrad B&G Navico & Garmin$30.00 -
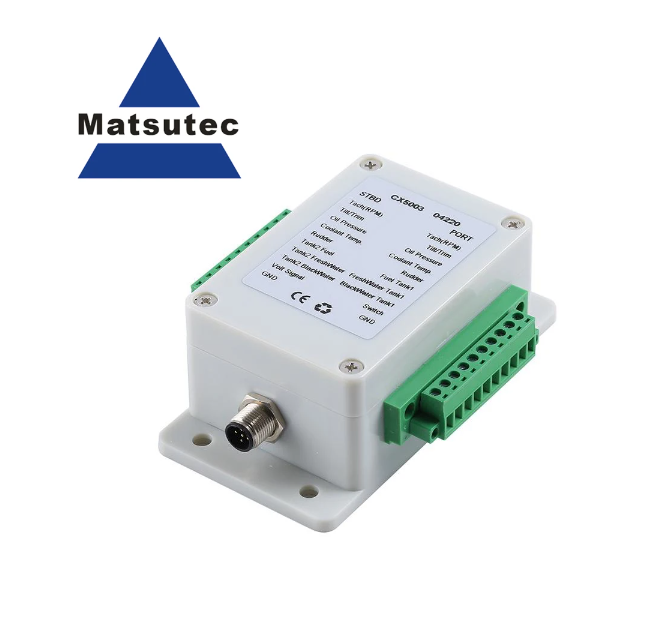 Matsutec NMEA2000 Converter Adapters CX5003 N2K Cables Sockets Multifunction Converter Connect Up to 5 Cables Lines Connector$200.00
Matsutec NMEA2000 Converter Adapters CX5003 N2K Cables Sockets Multifunction Converter Connect Up to 5 Cables Lines Connector$200.00 -
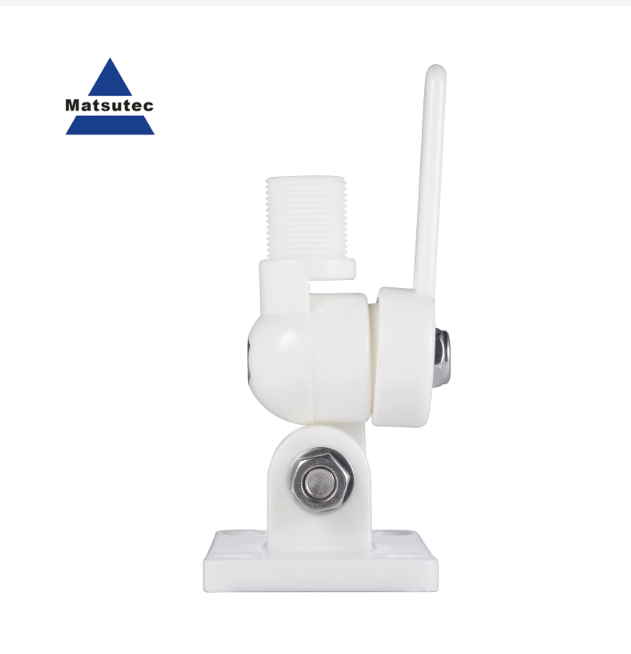 Matsutec SP002 Ship Antenna Base For GPS Antenna or VHF AIS Antenna$30.00
Matsutec SP002 Ship Antenna Base For GPS Antenna or VHF AIS Antenna$30.00 -
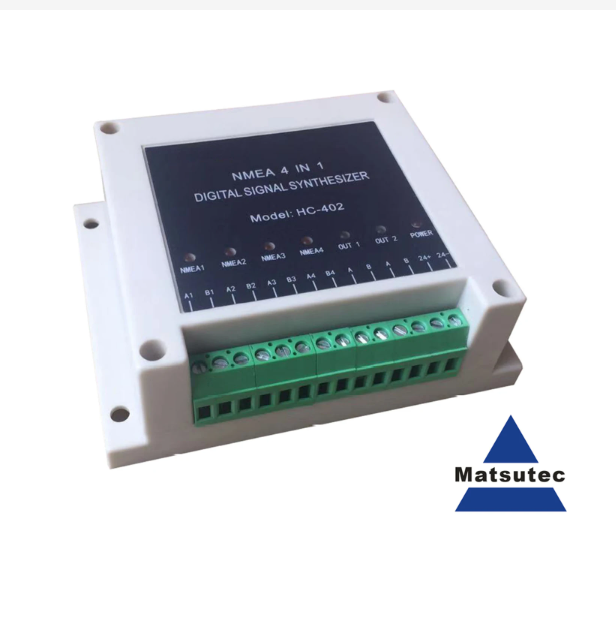 Matsutec HC-402 NMEA Multiplexer NMEA Digital Signal Synthesizer 4 in 1, input 4 Channel NMEA0183, Output 1 Channel NMEA0183.$300.00
Matsutec HC-402 NMEA Multiplexer NMEA Digital Signal Synthesizer 4 in 1, input 4 Channel NMEA0183, Output 1 Channel NMEA0183.$300.00 -
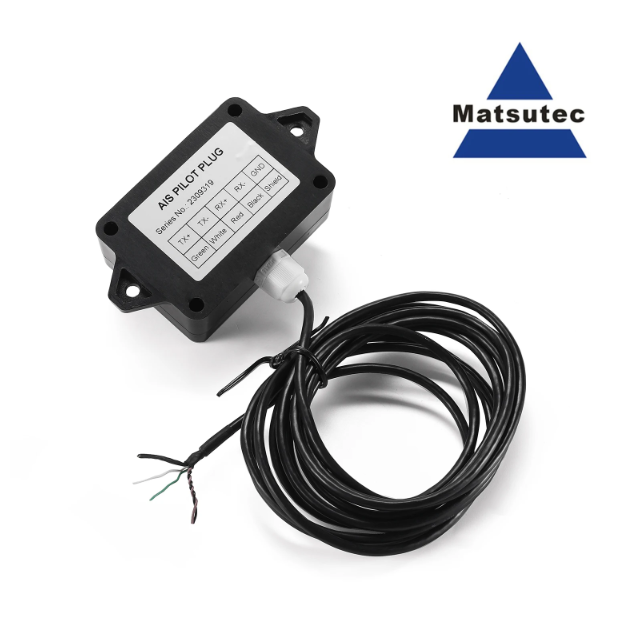 Matsutec NPC-160 AIS Pilot Plug data cable 3 Meter AIS Pilot Plug is an IMO Standard AIS Pilot Plug used for AIS RS422$120.00
Matsutec NPC-160 AIS Pilot Plug data cable 3 Meter AIS Pilot Plug is an IMO Standard AIS Pilot Plug used for AIS RS422$120.00 -
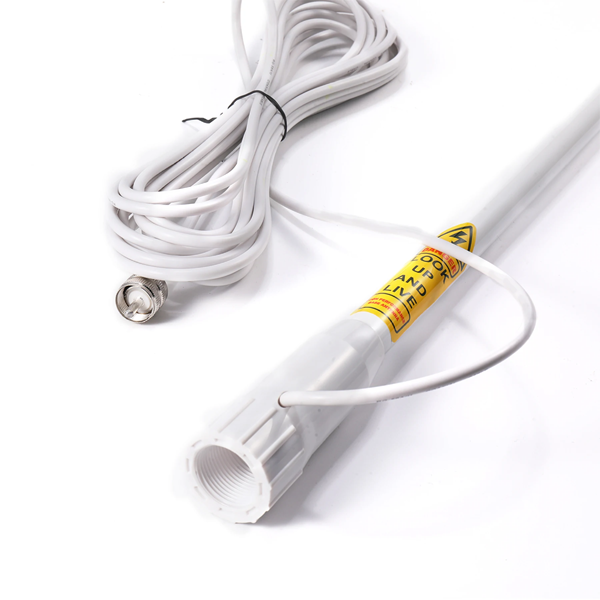 Matsutec HA-021 VHF antenna AIS antenna with 7m Cable and Fix support for yacht For Shipborne antenna$100.00
Matsutec HA-021 VHF antenna AIS antenna with 7m Cable and Fix support for yacht For Shipborne antenna$100.00 -
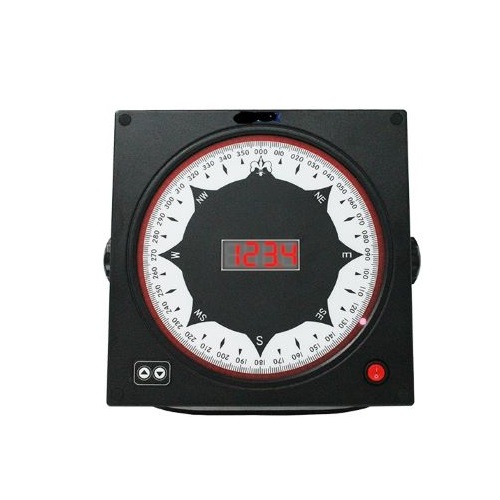 Matsutec Digit Compass Repeater DGR-160D$600.00
Matsutec Digit Compass Repeater DGR-160D$600.00 -
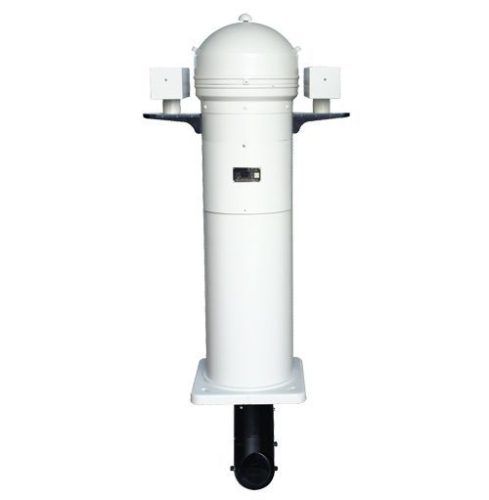 Matsutec Projection Magnetic Compass$850.00
Matsutec Projection Magnetic Compass$850.00 -
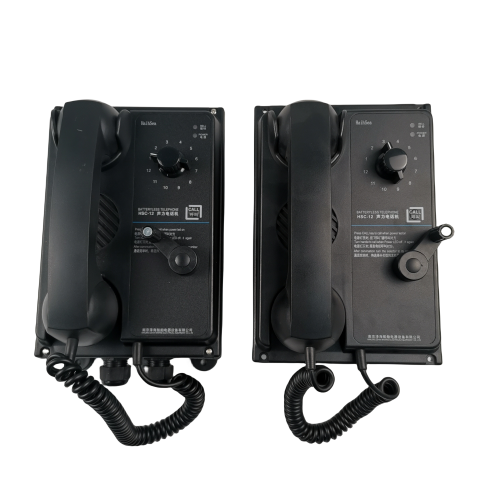 Battery less Telephones System HSC series$600.00
Battery less Telephones System HSC series$600.00 -
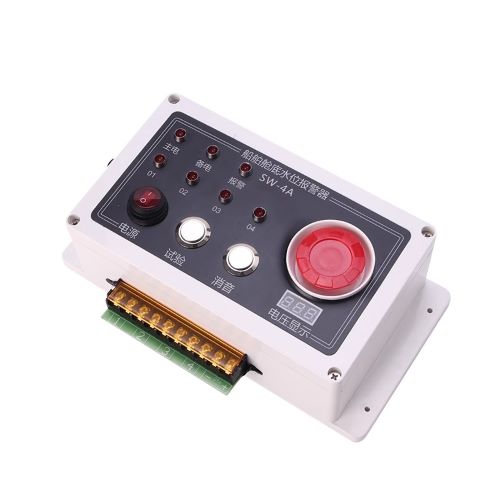 High Sensitivity Water level alarm$600.00
High Sensitivity Water level alarm$600.00 -
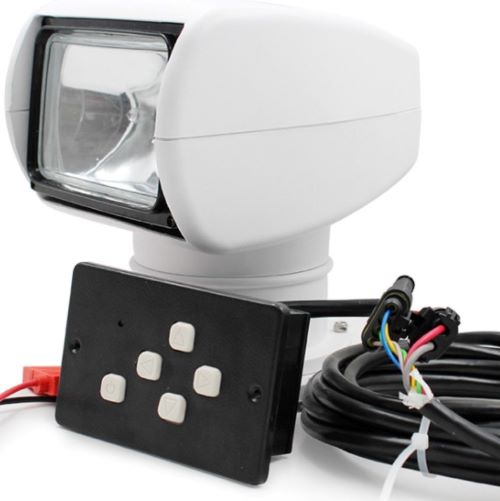 Yatching Remote Control 100W Searching Light$600.00
Yatching Remote Control 100W Searching Light$600.00 -
 Matsutec Marine Inclinometer$50.00
Matsutec Marine Inclinometer$50.00 -
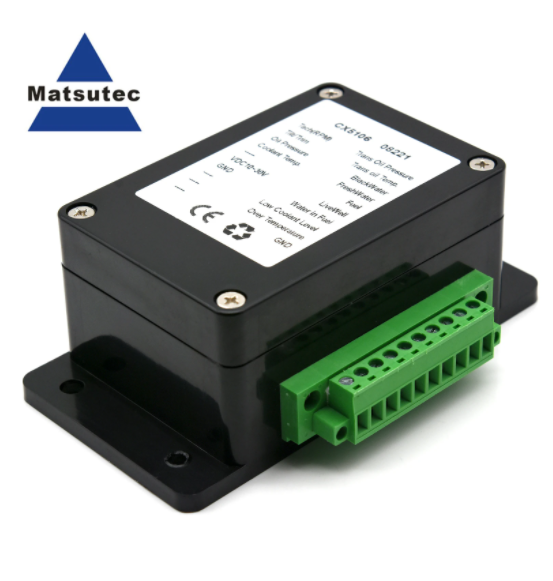 CX5106 NMEA 2000 Starter Kit Balck NMEA2000 Converter For Marine Boat Yacht Tank Gauge 0.5 Meter Line Accessories Tool$0.00
CX5106 NMEA 2000 Starter Kit Balck NMEA2000 Converter For Marine Boat Yacht Tank Gauge 0.5 Meter Line Accessories Tool$0.00 -
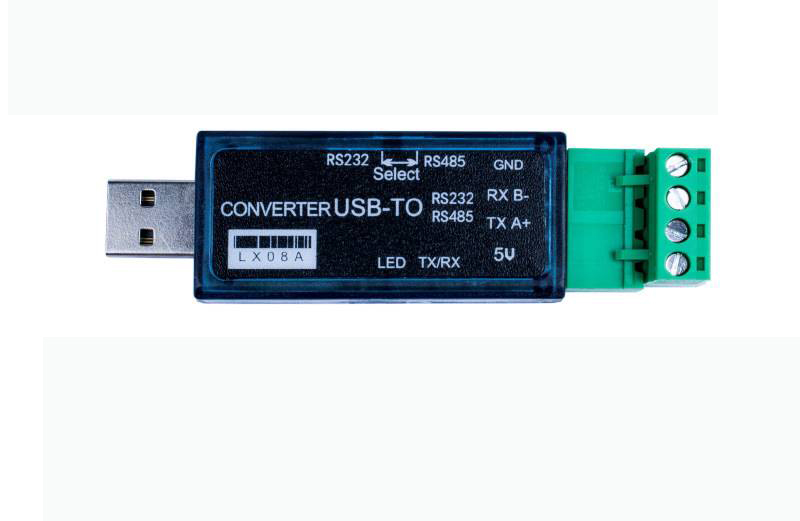 LX08A USB to 485, USB to 232 USB to RS232 485 Double Function Converter two-way transparent transmission 500m serial cable$100.00
LX08A USB to 485, USB to 232 USB to RS232 485 Double Function Converter two-way transparent transmission 500m serial cable$100.00 -
 ONWA KRI-80S Rudder Indicator Analog Rudder Angle indication system Suitable for all kind of vessels$0.00
ONWA KRI-80S Rudder Indicator Analog Rudder Angle indication system Suitable for all kind of vessels$0.00 -
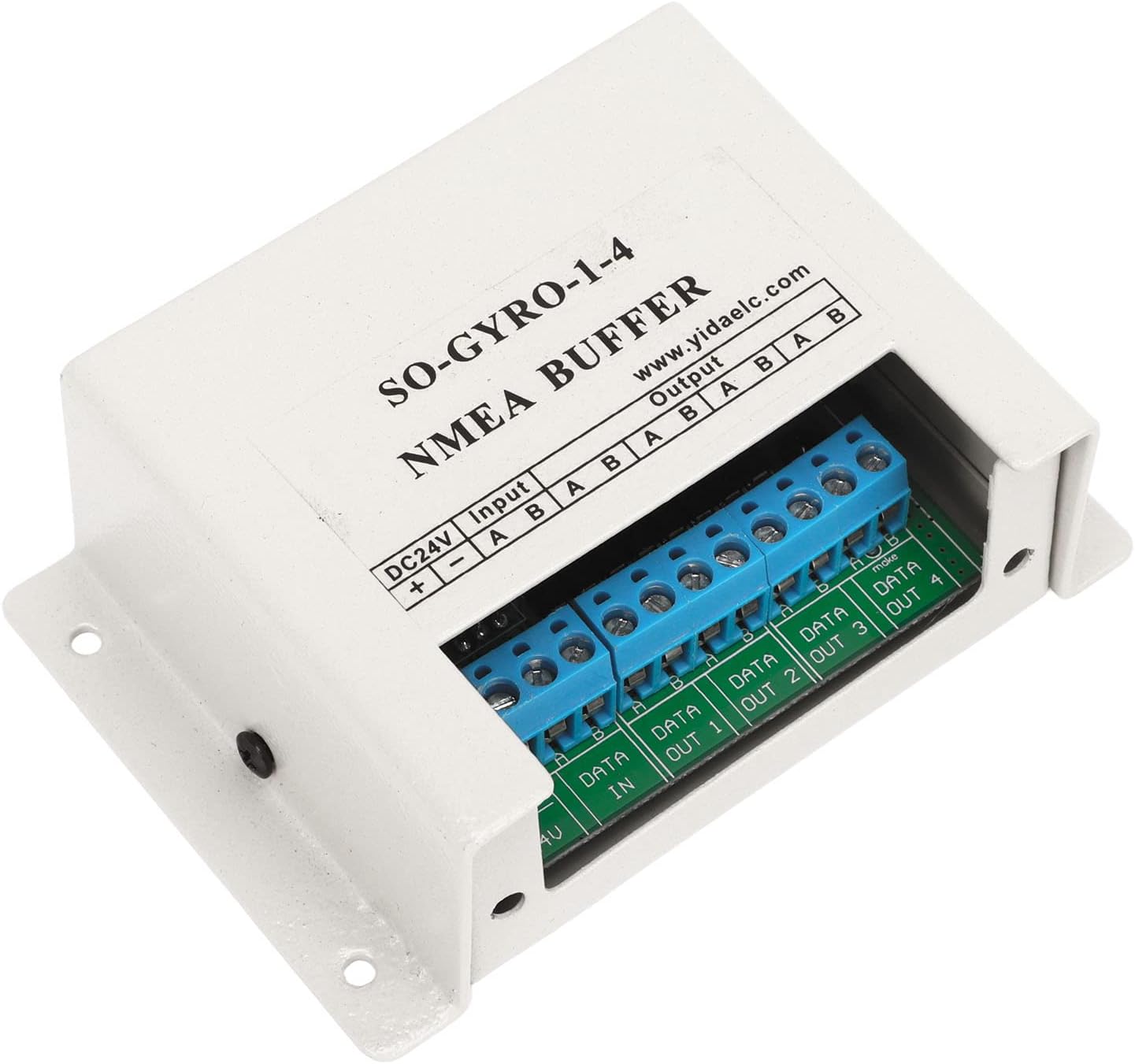 Matsutec NMEA0183 NMEA Buffer SY-1-4 NMEA 1 input, 4 output Marine Serial Line Splitter Isolating Buffer for 24V Circuit Systems$225.00
Matsutec NMEA0183 NMEA Buffer SY-1-4 NMEA 1 input, 4 output Marine Serial Line Splitter Isolating Buffer for 24V Circuit Systems$225.00 -
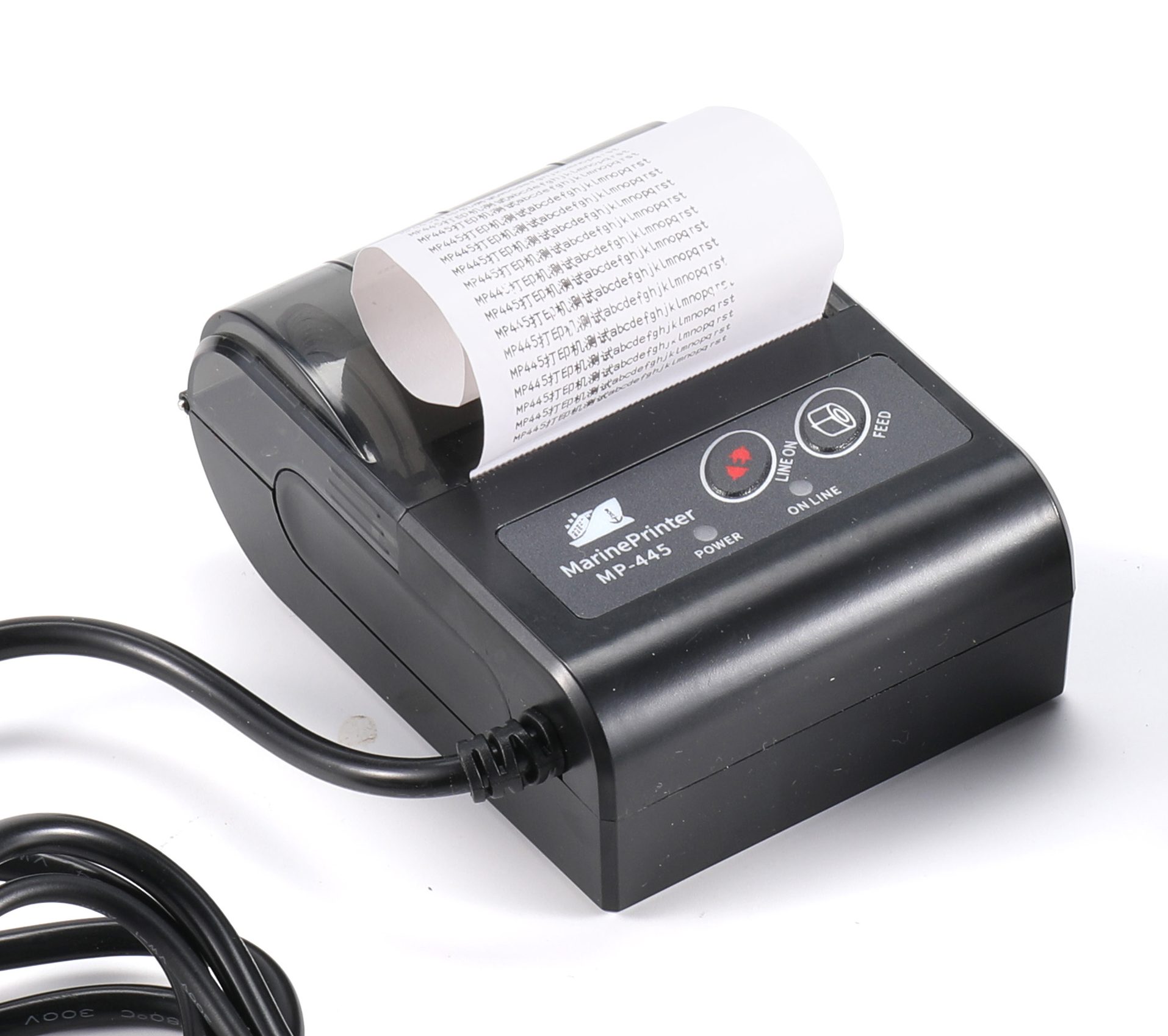 MP445 printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor GMDSS NAVTEX RECEIVER THERMAL PRINTER$325.00
MP445 printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor GMDSS NAVTEX RECEIVER THERMAL PRINTER$325.00 -
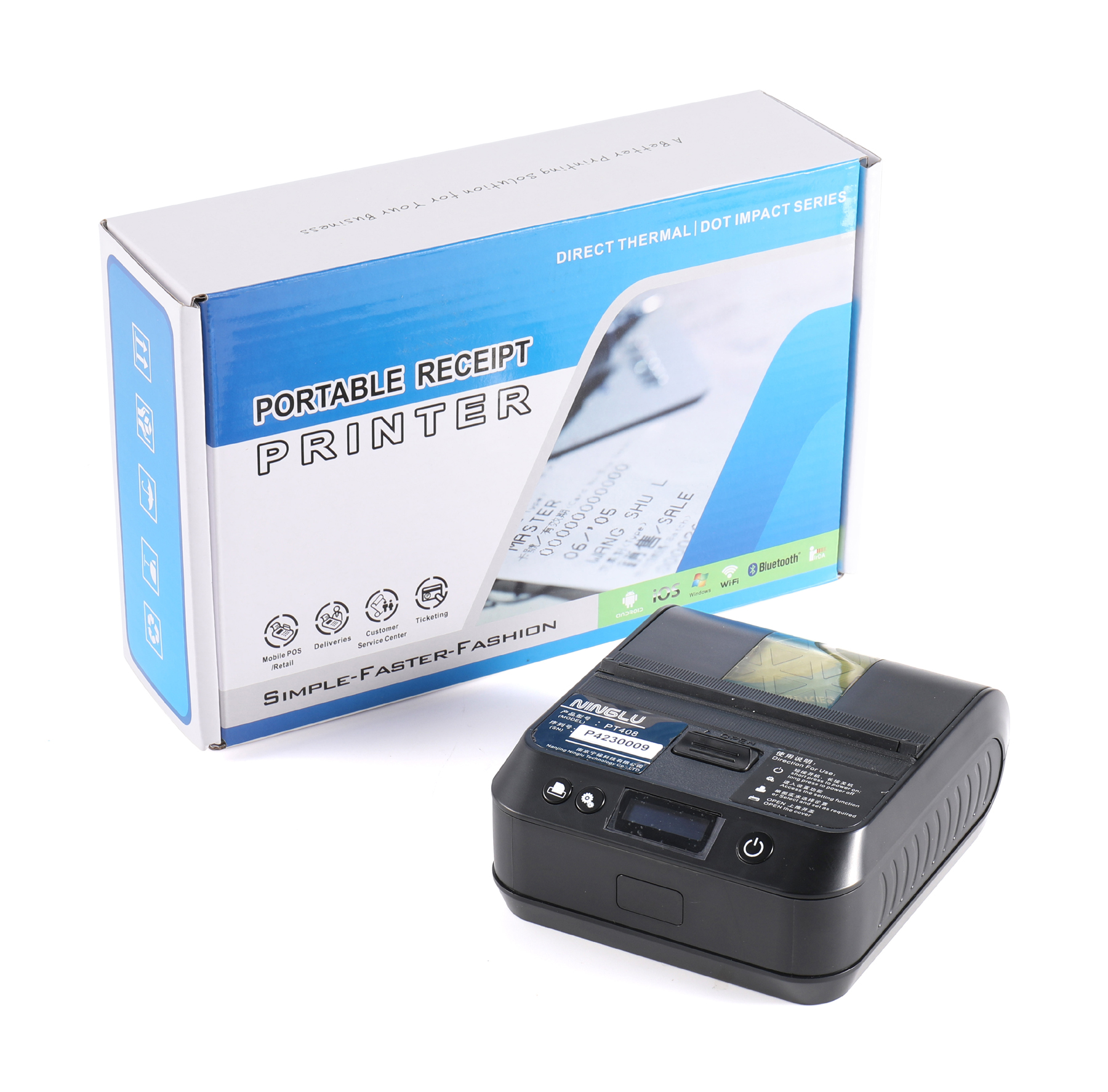 PT408 Thermal printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor can be connected to anemometer AM706$350.00
PT408 Thermal printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor can be connected to anemometer AM706$350.00 -
 Matsutec STR-01 Satellite Phone Indoor GPS Repeater / Amplifier Device (Inmarsat & Thuraya Suitable)$850.00
Matsutec STR-01 Satellite Phone Indoor GPS Repeater / Amplifier Device (Inmarsat & Thuraya Suitable)$850.00 -
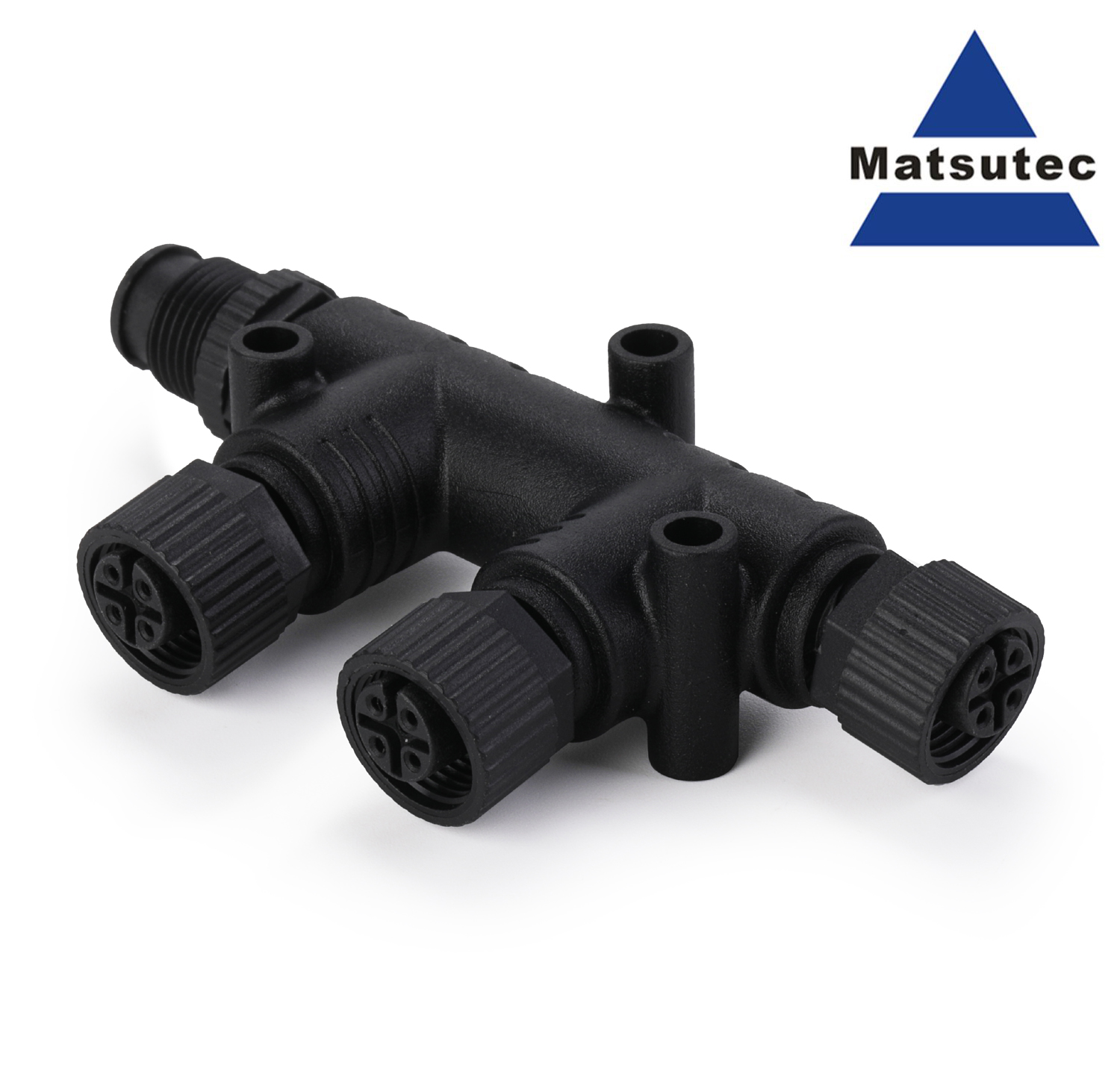 NMEA 2000 T Connector 4 Port 5Pin M12 Thread IP67 Waterproof NMEA 2000 (N2k) (Tee) T-Connector for Garmin Lowrance Simrad B&G$25.00
NMEA 2000 T Connector 4 Port 5Pin M12 Thread IP67 Waterproof NMEA 2000 (N2k) (Tee) T-Connector for Garmin Lowrance Simrad B&G$25.00 -
 For NMEA 2000 4 Port T Connector, For NMEA 2000 N2K 4 Ports Tee Connector M12 5 Pin IP67 Waterproof$55.00
For NMEA 2000 4 Port T Connector, For NMEA 2000 N2K 4 Ports Tee Connector M12 5 Pin IP67 Waterproof$55.00 -
 NPT-100 NSR Thermal printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor$600.00
NPT-100 NSR Thermal printer for NAVTEX Receiver with power adaptor$600.00 -
 Boat Transducer Fishfinder Price A-B117 600W 50/200khz Bronze Thru-hull Fishing Transducer Support NMEA0183 protocol$600.00
Boat Transducer Fishfinder Price A-B117 600W 50/200khz Bronze Thru-hull Fishing Transducer Support NMEA0183 protocol$600.00 -
 RS-509MG VHF Fixed Marine Radio with GPS$500.00
RS-509MG VHF Fixed Marine Radio with GPS$500.00 -
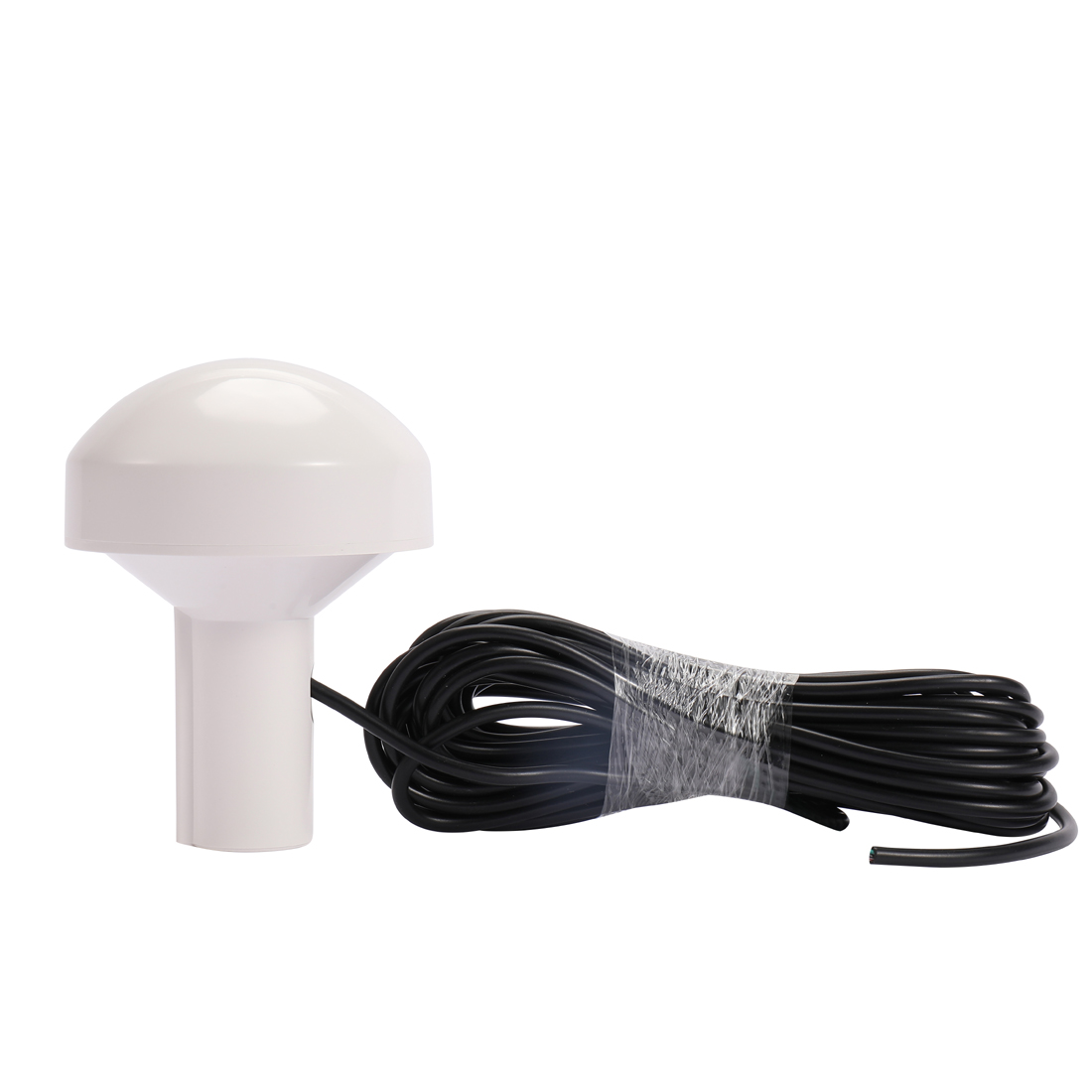 Matsutec HA-017M marine GPS Receiver Antenna with NMEA0183 RS232 output nmea 0183 gps antenna$300.00
Matsutec HA-017M marine GPS Receiver Antenna with NMEA0183 RS232 output nmea 0183 gps antenna$300.00 -
 Matsutec S82 Power Source 220WH$2700.00
Matsutec S82 Power Source 220WH$2700.00 -
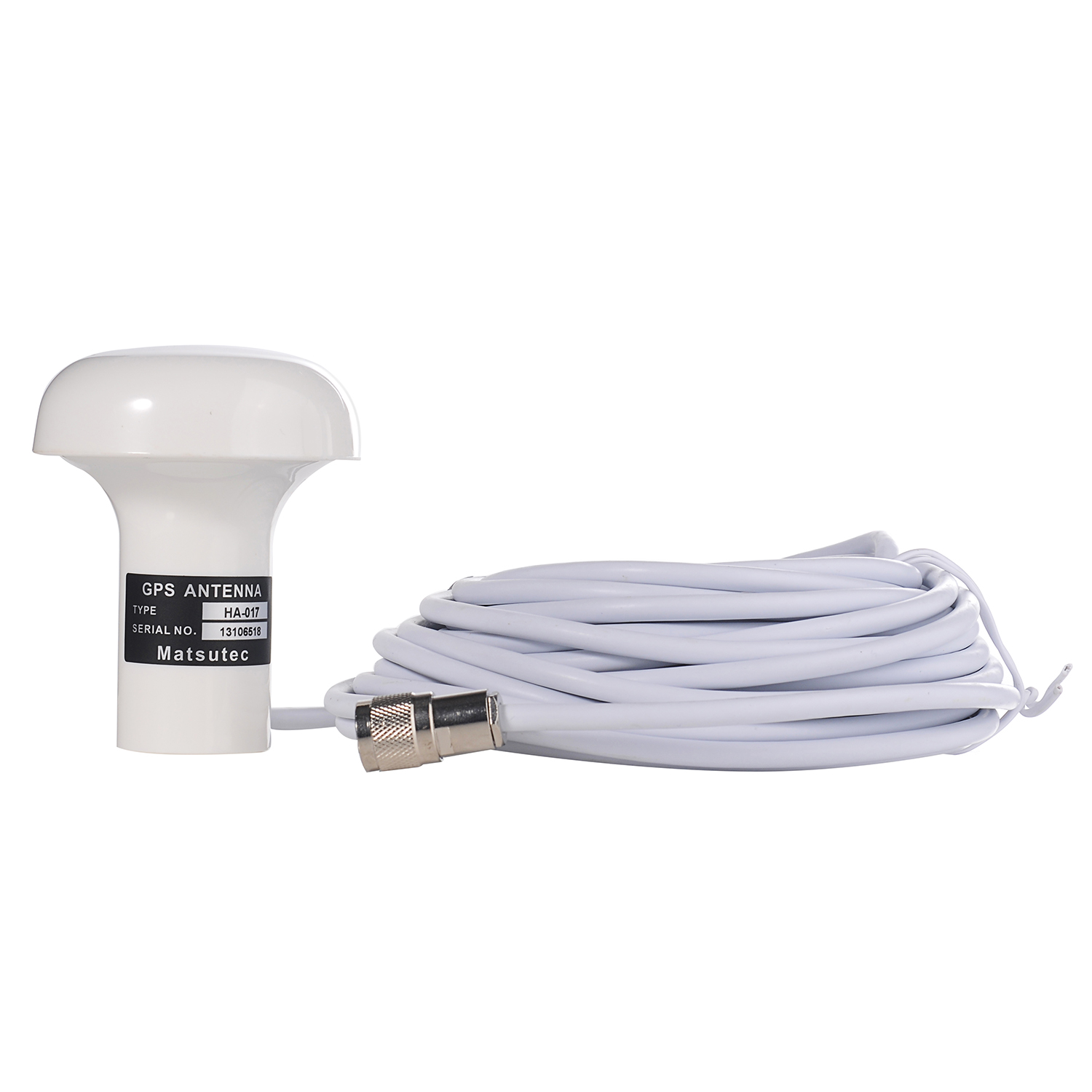 Matsutec HA-017 Marine GPS Antenna$980.00
Matsutec HA-017 Marine GPS Antenna$980.00 -
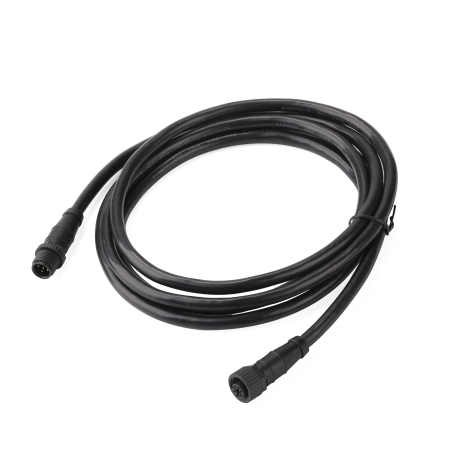 Matsutec 0.5Meter 5pin NMEA 2000 (N2K) 1/2 Meter, Backbone or Drop, Cable$25.00
Matsutec 0.5Meter 5pin NMEA 2000 (N2K) 1/2 Meter, Backbone or Drop, Cable$25.00 -
 Matsutec 1 Meter 5pin NMEA 2000 (N2K) 1 Meter, Backbone or Drop, Cable$30.00
Matsutec 1 Meter 5pin NMEA 2000 (N2K) 1 Meter, Backbone or Drop, Cable$30.00 -
 Matsutec NMEA 2000 (N2k) (Tee) T-Connector for Garmin Lowrance Simrad B&G & Navico Networks$25.00
Matsutec NMEA 2000 (N2k) (Tee) T-Connector for Garmin Lowrance Simrad B&G & Navico Networks$25.00



